
Vitamin D Deficiency:
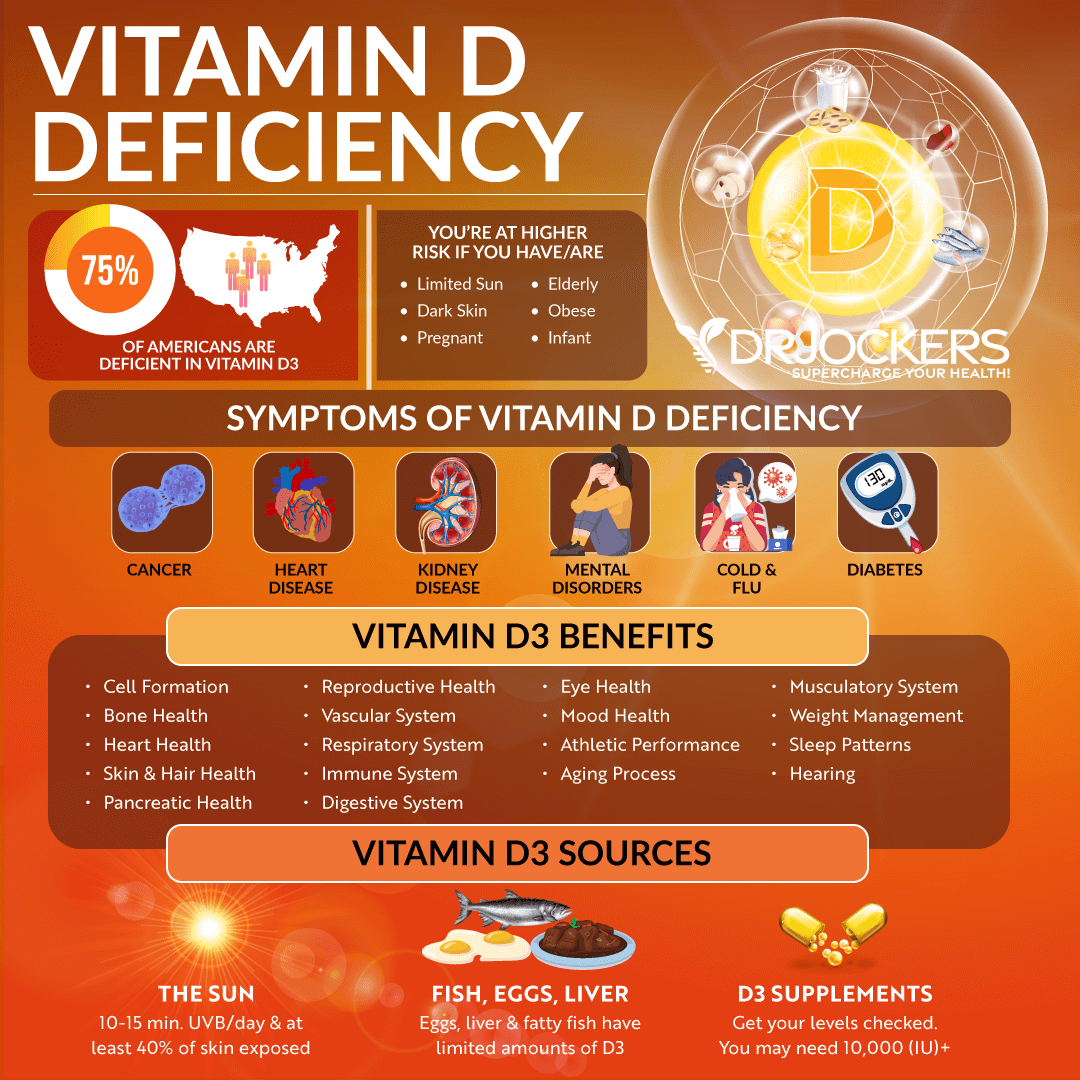
One of the most common health problems in the world today is vitamin D deficiency. Around 3 billion people worldwide and 75-80% of Americans are deficient in this important vitamin.
A vitamin D deficiency is associated with multiple chronic conditions including the leading causes of mortality. Vitamin D deficiencies have been found to play a role in many conditions including cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, osteoporosis, and many other health conditions. Having optimal levels of vitamin D is critical for good overall health.
Vitamin D is often called the “sunshine vitamin” because the primary source of Vitamin D is exposure to the sun. When sun exposure is limited, it is important to obtain vitamin D from other sources. The best food sources of vitamin D are egg yolks, fatty fish, liver, and grass-fed cheese and butter.
However, for many people, supplementation may be necessary to increase their levels of vitamin D to optimal levels. It is important to test your level of vitamin D regularly to ensure it is optimal and to prevent health issues associated with deficiencies.
What is Vitamin D?
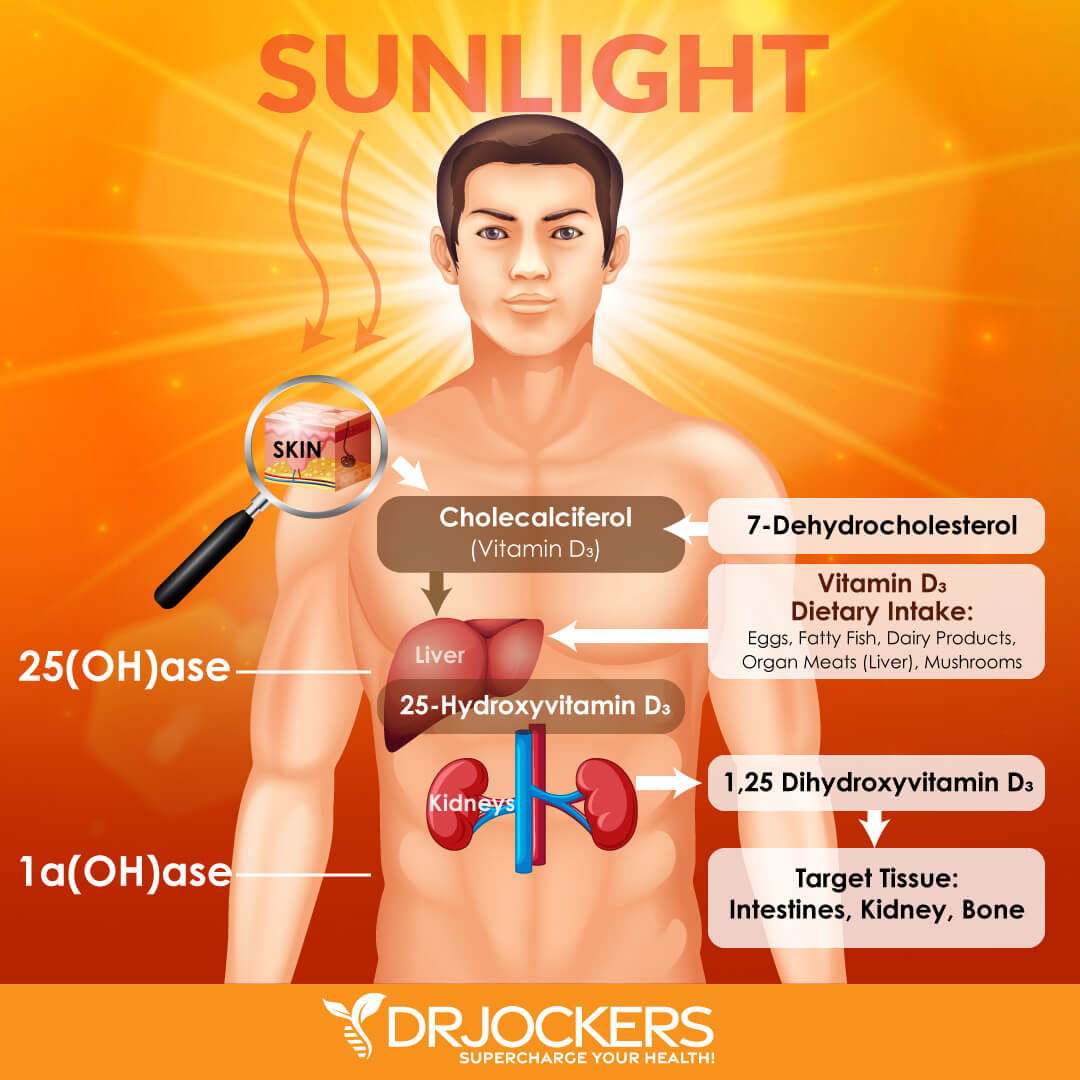
Vitamin D is unique in that it functions as a prohormone (1). Prohormones are substances that the body converts to a hormone.
Vitamin D is the only vitamin that can be produced by our bodies (2). While other vitamins must be taken in through diet or supplementation, our bodies produce vitamin D when our skin is exposed to UV rays from the sun.
Vitamin D obtained from sun exposure, food, and supplements is biologically inert and must be activated by the body. Two hydroxylations are required for activation. The first occurs in the liver and converts vitamin D to 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D], or calcidiol. The second occurs primarily in the kidneys and forms the physiologically active 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D], or calcitriol (“activated vitamin D”).
Vitamins are either water soluble or fat soluble. Vitamin D, along with vitamins A, E, and K, are fat soluble which means they need a source of fat to be absorbed. Fat soluble vitamins can accumulate in the body’s tissue.
Serum 25(OH)D is the best marker of vitamin D status (3). It reflects vitamin D produced by the body and that is obtained from food and supplements. 25(OH)D has a circulating half-life of 15 days.
Two Types of Vitamin D
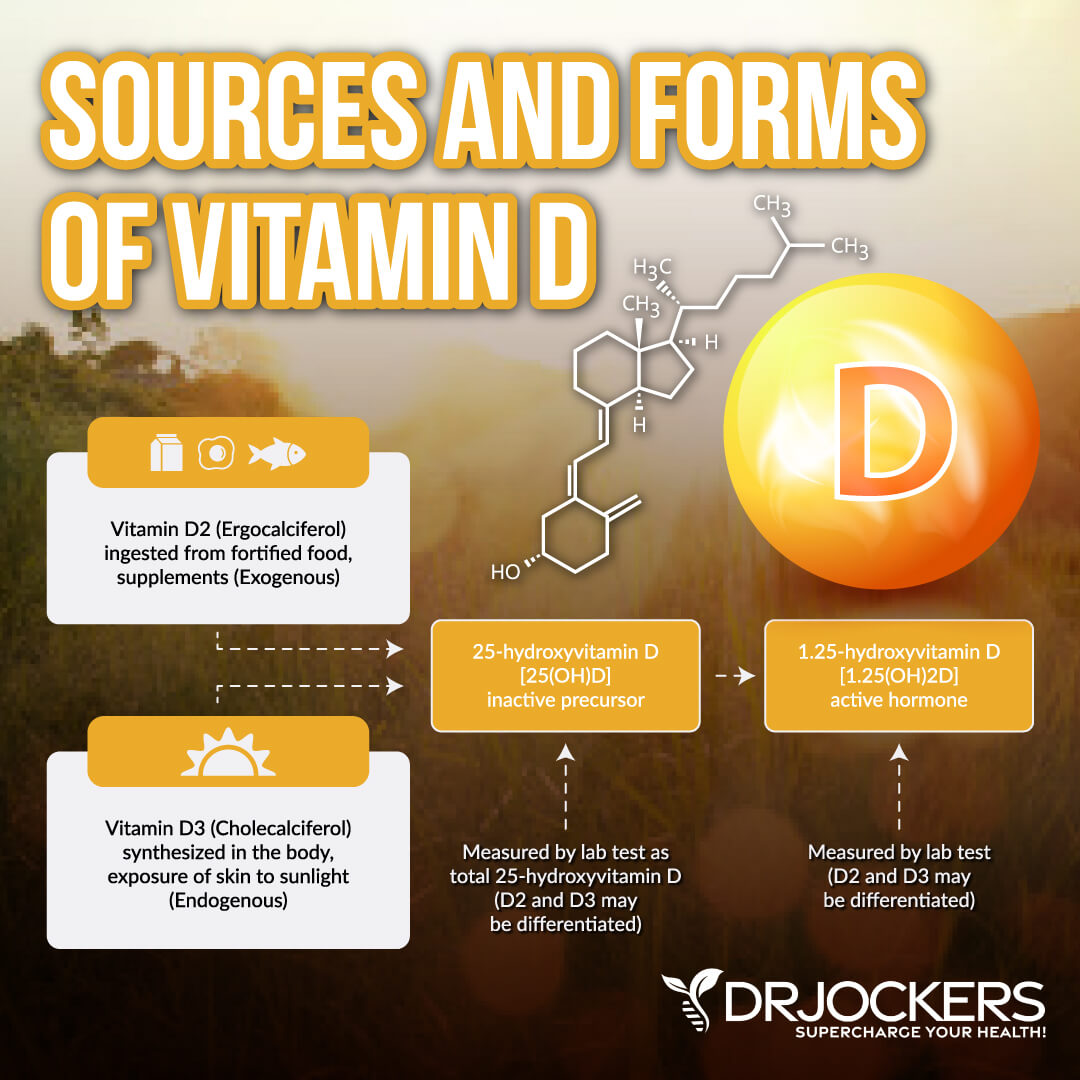
There are two main types of vitamin D, D2 and D3. They are different in several ways.
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is sourced from the UV irradiation of ergosterol. Ergosterol is a steroid found in some plants but largely in fungi. The best source of D2 is mushrooms grown in UV light. D2 is synthesized by plants and is not produced by the body.
- Vitamin D3 (or cholecalciferol) is synthesized by UV irradiation of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3. Specifically, ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation from sunlight triggers the formation of vitamin D3. D3 is also found in animal-sources such as salmon, egg yolks, and beef.
Both D2 and D3 must be converted into active compounds through the same two-step process, resulting in calcitriol. Studies have shown that vitamin D3 has a more significant and positive effect in raising serum 25(OH)D concentrations than D2 (1).
Why is Vitamin D So Important?
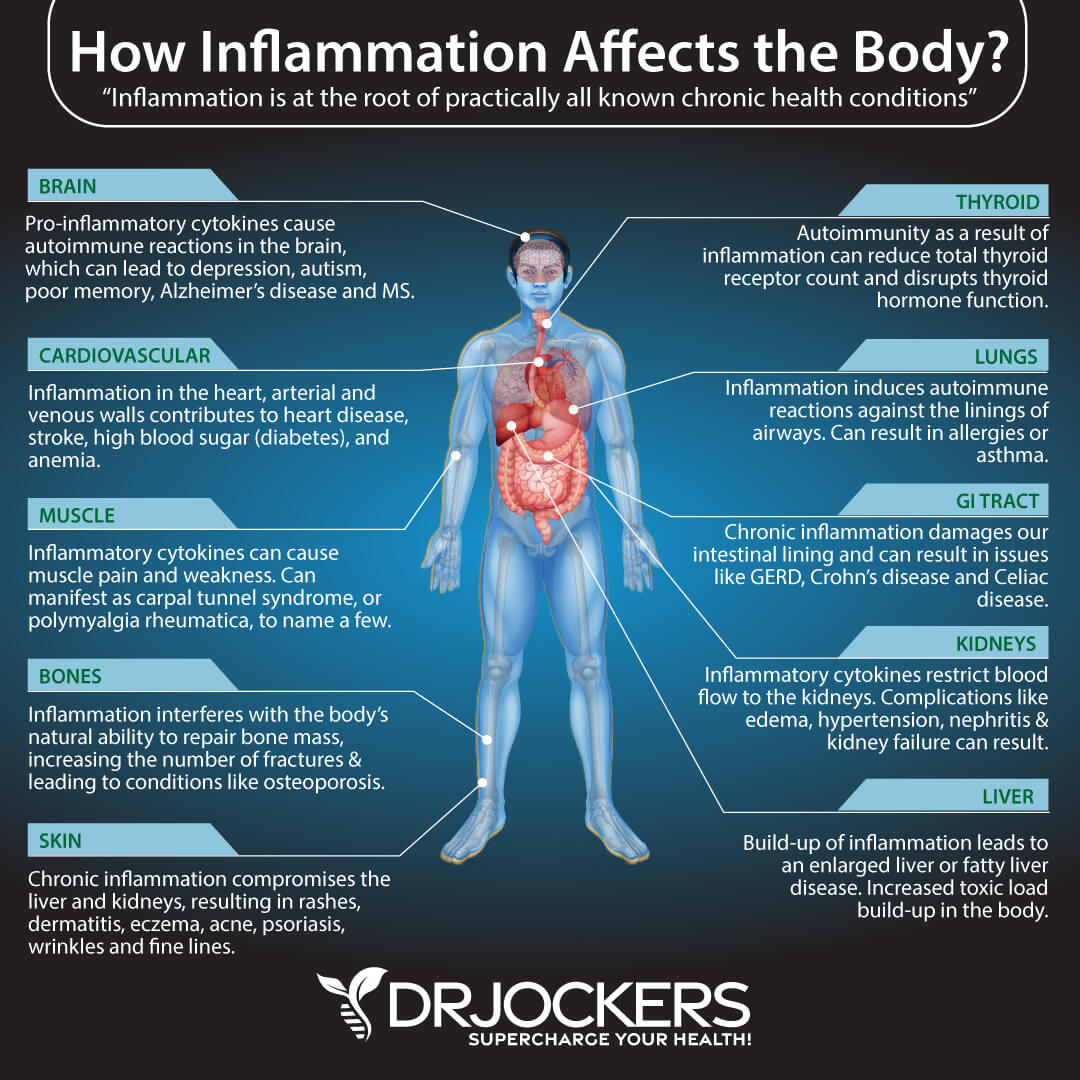
Vitamin D plays an important role in overall health and well-being. It is best known for promoting bone health and healthy calcium metabolism, but researchers have found that vitamin D is critical for all systems of the body.
Vitamin D plays a central role in the immune system, muscle function, cardiovascular function, respiratory system, and brain development. Once activated, Vitamin D works by managing calcium in your blood, bones, and gut. It also helps cells all over the body communicate properly. Here are some of the ways vitamin D benefits the body.

1. Modulates The Immune System
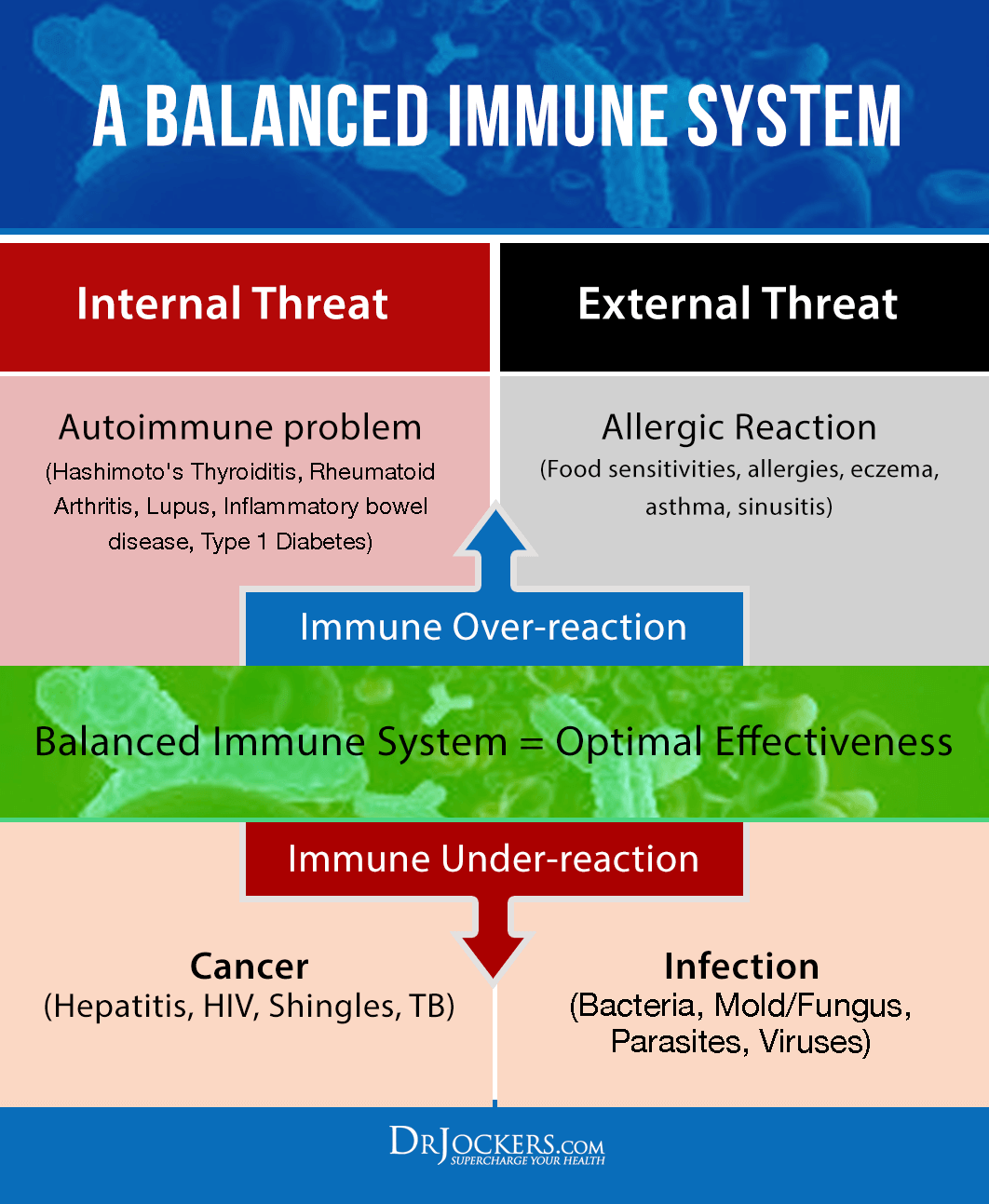
Vitamin D plays an important role in both innate and adaptive immune responses. The active form of Vitamin D plays a key role in maintaining immune homeostasis.
D3 is an immunomodulator targeting various immune cells, including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, as well as T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes. Several epidemiological studies have linked inadequate vitamin D levels to a higher susceptibility to immune-mediated disorders including chronic infections and autoimmune diseases (4).
An autoimmune condition occurs when the body’s immune system malfunctions. It mistakenly identifies healthy cells and tissues as foreign invaders and starts attacking and destroying them. This can happen in almost any part of the body, including the brain, muscles, skin, and other organs. Autoimmune diseases associated with low vitamin D include multiple sclerosis (MS), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), diabetes mellitus (DM), inflammatory bowel disease, and lupus.
2. Protects Against Cancer
Vitamin D has demonstrated cancer-protective and anti-cancer properties (5). These properties include triggering apoptosis (programmed cell death), inhibiting cancer cell growth, and reducing metastatic potential.
Multiple studies show an increased risk of cancers, including colon, breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers, among people with vitamin D deficiency (6). Studies have also linked higher levels of vitamin D with a lowered risk of certain cancers and a better cancer outcome.

3. Induces Autophagy
Vitamin D3 is a key hormonal inducer of autophagy. Autophagy is your intracellular recycling system and cellular self-degradation process where your body cleans out debris and recycles damaged cell components. This leads to the regeneration of cells.
Cells use autophagy to maintain biological function, homeostasis, quality-control of cell contents, and to eliminate old proteins and damaged lipids and organelles. Autophagy enables cells to survive external stressors like nutrient deprivation and internal stressors like pathogens.
Vitamin D signaling can regulate autophagy at different levels, including induction, nucleation, elongation to maturation, and degradation (7). To learn more about autophagy and ways to enhance it, read this article.

4. Prevents Cognitive Decline
Dementia is a syndrome (group of symptoms), usually chronic and progressive, associated with the loss of memory and other cognitive functions (8). It is caused by different brain illnesses that affect thinking, orientation, comprehension, calculation, learning capacity, language, judgment, behavior, and memory without a lack of consciousness. These symptoms are severe enough to interfere with a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks.
Numerous studies have shown that vitamin D may reduce the risk of cognitive decline. In a 2014 study, researchers found that vitamin D deficiency is associated with a substantially increased risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s (9). Individuals with severe vitamin D deficiency (less than 10 ng/mL) had a 122% increased risk of dementia and Individuals deficient (less than 20 ng/mL) in vitamin D had a 51% risk of dementia. Vitamin D3 has neuroprotective effects including the clearance of amyloid plaques.

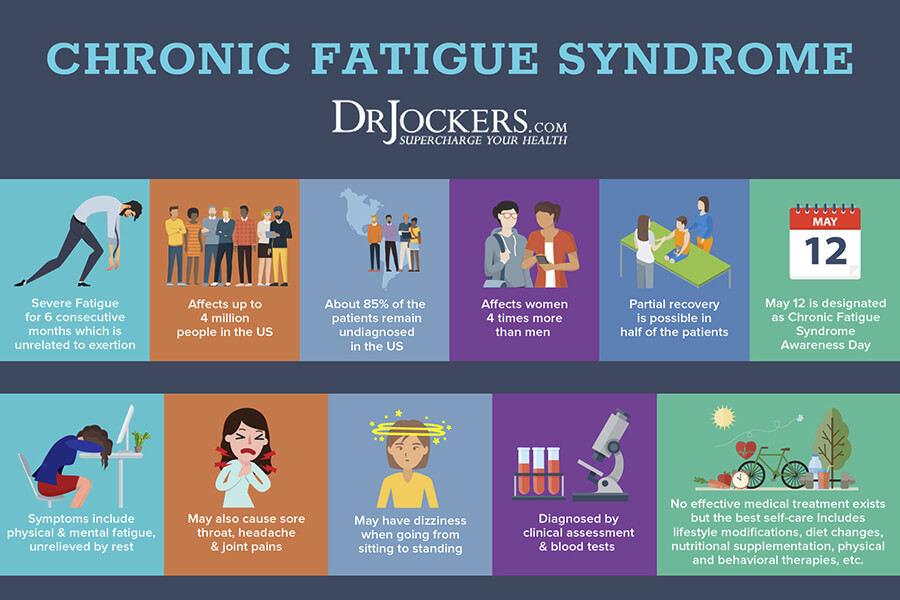
5. Improves Chronic Fatigue
Low vitamin D levels are highly prevalent in people with chronic fatigue (10). Chronic fatigue is when you are tired, worn out, drained, and depleted most of the time.
This profound and unrelenting exhaustion typically develops over time and it can be hard to pinpoint when it first started (11). It impacts your physical, emotional, and psychological well-being. Optimizing your vitamin D levels can improve chronic fatigue.
6. Promotes Bone Health
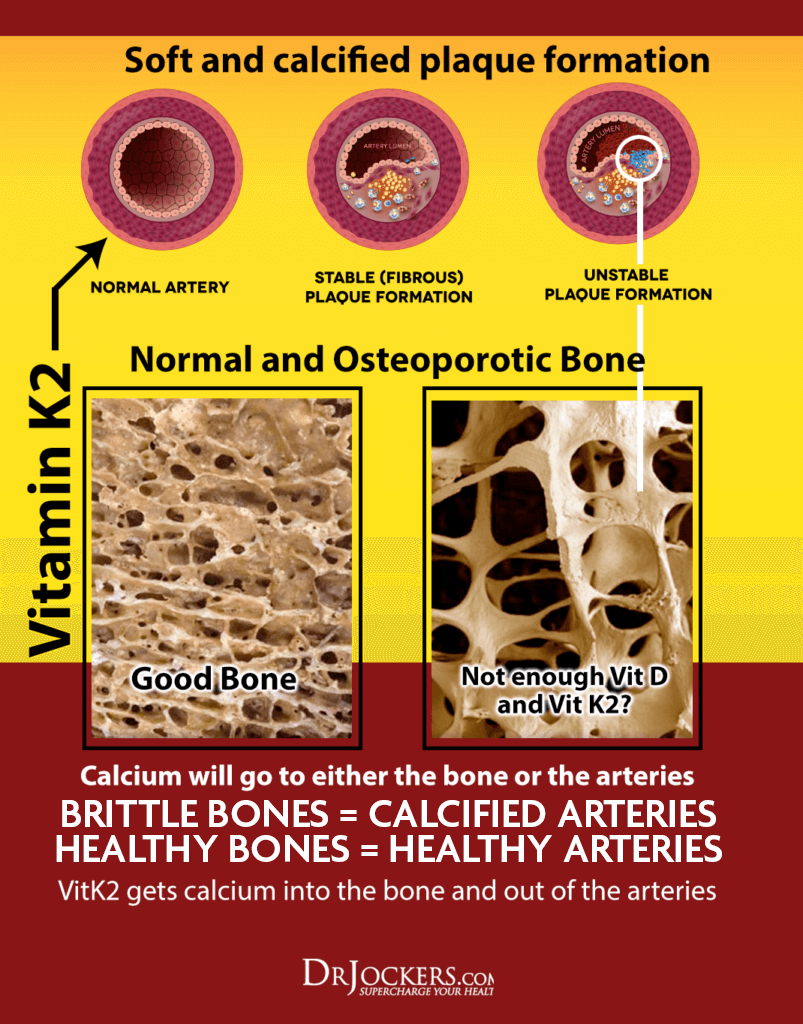
Vitamins D3 and K2 work synergistically to promote bone health and reduce the incidence of fractures (12). They work synergistically to play an essential role in calcium uptake into skeletal bone tissue. This can help to prevent osteoporosis and osteopenia which occur when bones become weak and lose minerals.
Osteocalcin is a bone-building protein that is necessary for maintaining calcium homeostasis in bone tissue. It works with osteoblast cells to build healthy bone tissue. The combination of vitamins D3 and K2 enhances the accumulation of osteocalcin greater than either nutrient alone. Increased osteocalcin formation significantly improves bone mineral density. D3 and K2 also work together to increase Matrix GLA protein (MGP), which protects blood vessels from calcification.
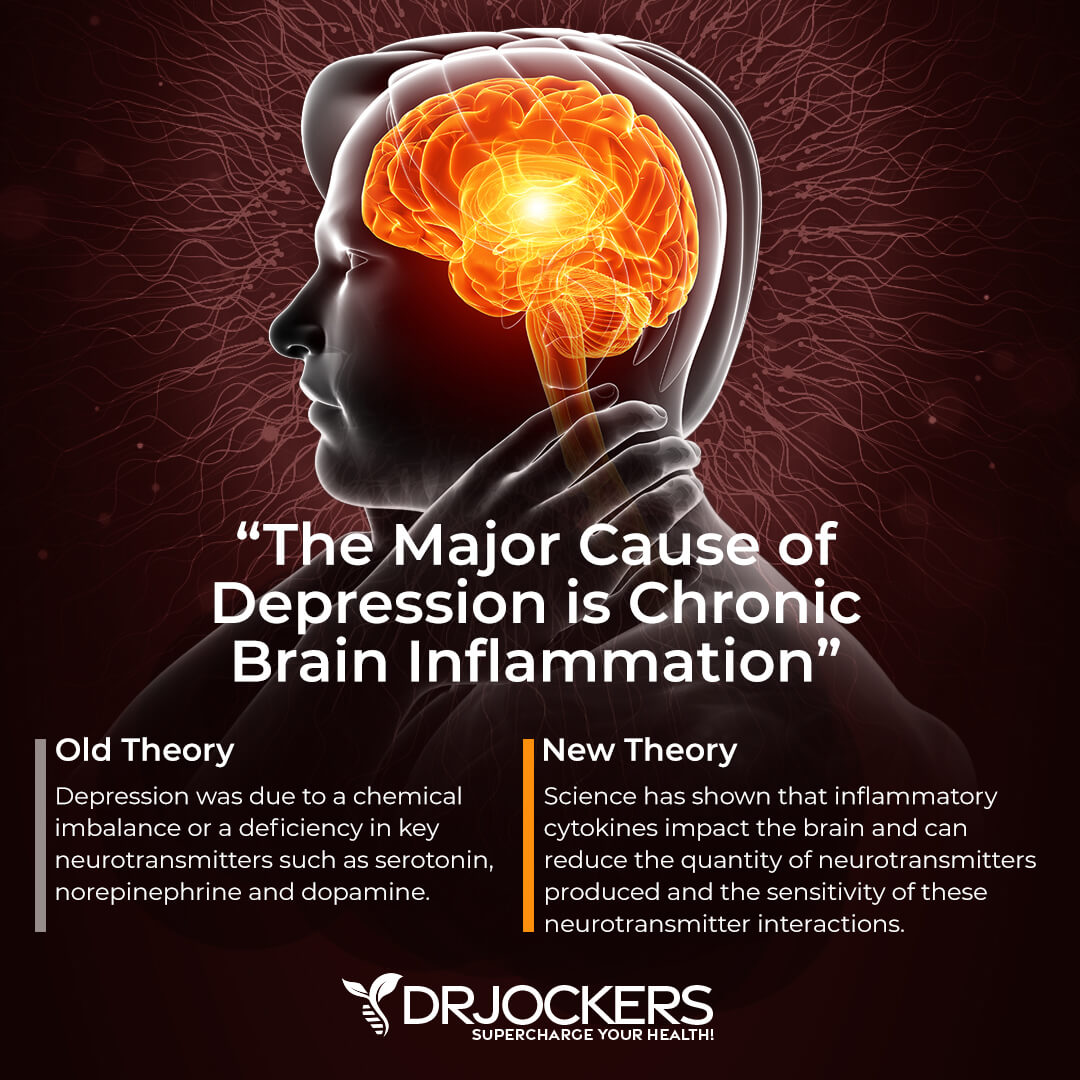
7. Improves Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are the most common mental health issues in the United States. Often experienced together, 40-60% of people with anxiety have signs of depression. Vitamin D is an important factor in the prevention and treatment of anxiety and depression (13).
Optimizing levels of certain nutrients like vitamin D is a natural strategy to improve anxiety, depression, and irritability. Along with vitamin D, important nutrients for optimal brain function and good mental health are magnesium, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C, iron, selenium, iodine, zinc, B vitamins, and amino acids. Correcting any deficiencies of these nutrients can improve or even eliminate your symptoms. This article discusses 14 nutrients for emotional support.
8. Reduces Joint Pain
Vitamin D is an important nutrient for healthy joints. Joint pain is discomfort, pain, or inflammation in any part of a joint. The underlying cause of joint pain is inflammation, and vitamin D is a key immunoregulator for inflammation.
Deficiencies in vitamin D have been linked to osteoarthritis and decreased cartilage thickness (14). Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis affecting around 10% of the American population. It occurs when the protective cartilage on the ends of your bones wears down over time leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and pain in the joints. To read about more natural strategies for improving joint pain, check out this article.
9. Sleep Apnea
Low vitamin D levels are linked to obstructive sleep apnea and the activation of numerous inflammatory processes (15). Sleep apnea is a common condition in which a person’s breathing is interrupted or paused during their sleep. Sleep apnea is most common in men and older people. This condition is linked to obesity, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, depression, and other health conditions.
Low levels of vitamin D can contribute to and worsen the impact of sleep apnea on glucose metabolism. Abnormal glucose metabolism is one of the main health issues associated with sleep apnea (16). Supplementing with vitamin D has been shown to improve abnormal glucose metabolism and inflammation in people with sleep apnea.

10. Prevent Endometriosis and PCOS
Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome (17) (18). Endometriosis is a painful condition where the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside of the uterine cavity. This displaced endometrial tissue leads to cysts, scar tissue, and adhesions. Endometriosis is a chronic and debilitating disease that affects around 10% of all women of reproductive age.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormone imbalance disorder and one of the most common endocrine disorders affecting women. This devastating health condition has a negative impact on a woman’s health, her ability to have a child, and her physical appearance. Around 70%-80% of women with PCOS are deficient in vitamin D. Low vitamin D levels are significantly correlated with insulin resistance in women with PCOS.

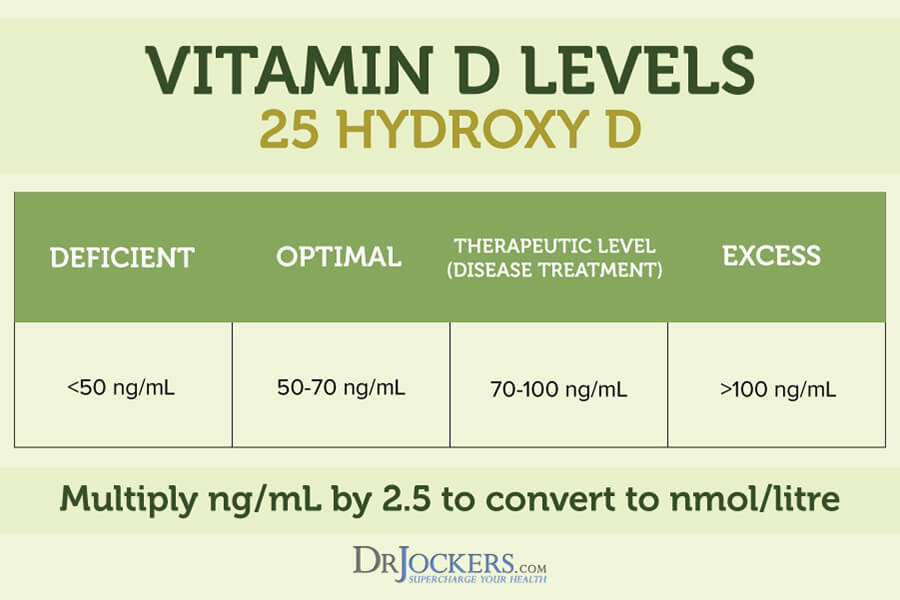
Optimal Levels of Vitamin D
In the medical world, vitamin D deficiency is measured by being under 30 ng/mL. Studies have found that around 40% of Americans are very deficient in Vitamin D (6). It is estimated that globally, about 1 billion people have low vitamin D levels. This is found in all ethnicities, genders, and age groups.
With vitamin D being so important to good health, deficiencies in vitamin D can have serious health consequences. Studies have shown that there is a relationship between deficiencies in vitamin D and greater all-cause mortality (19).
In a 2011 study, researchers estimated that doubling vitamin D levels would reduce the vitamin D-sensitive disease mortality rate by 20%. Researchers concluded that increasing serum Vitamin D levels is the most cost-effective way to reduce global mortality rates (20).
Major risk factors for vitamin D deficiency include inadequate sunlight exposure, inadequate intake of foods that contain vitamin D, and malabsorption syndromes such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease (6).
From a functional health perspective, being at 35 ng/mL, although not considered deficient, is not optimal for overall health. The ideal range for your vitamin D3 level is between 50-100 ng/ml. At this level, the risk for chronic inflammatory diseases is significantly reduced. Many experts believe a therapeutic level of vitamin D is between 70-100 ng/mL.
Healthy Sun Exposure
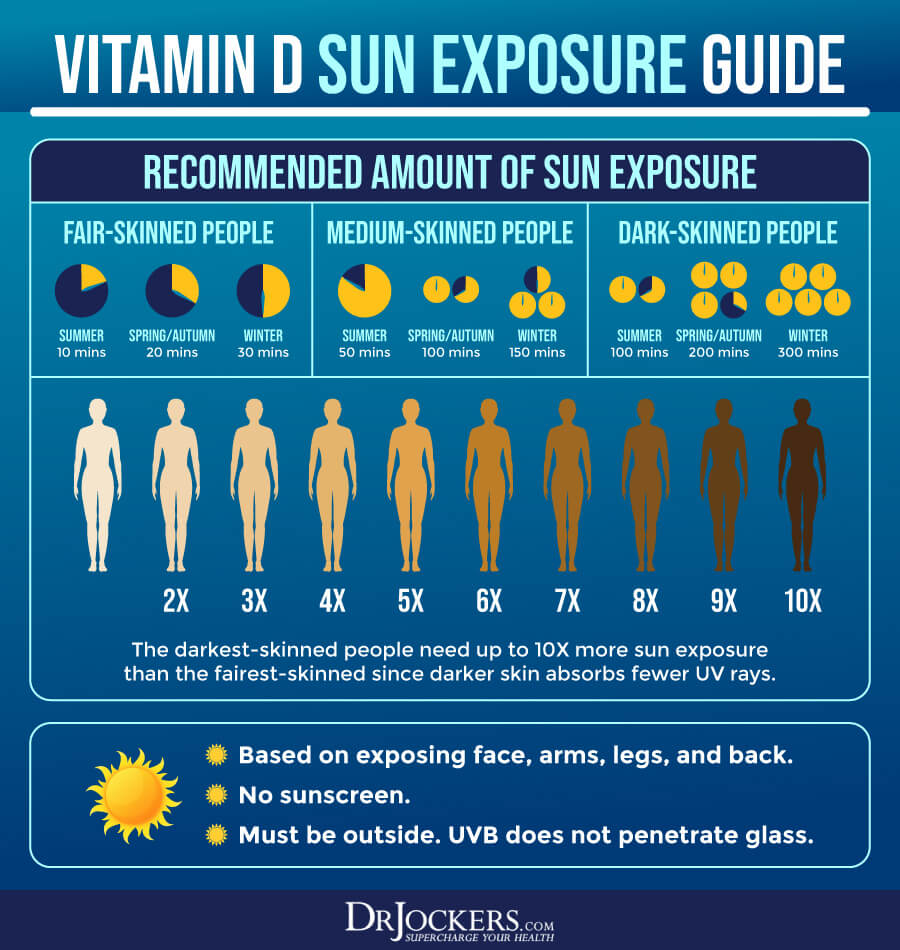
The sun is the best source of vitamin D. In areas where there is sufficient UVB exposure, there are several factors to consider in determining how much sun exposure is appropriate. These factors include the portion of skin exposed to the sun, the color of your skin, and the strength of the UV rays. If 60% of the body is exposed to the sun, it is ideal to seek 10,000 to 20,000 IU of vitamin D3 from sun exposure.
Intentionally sunbathe no less than 3 times per week according to the following recommendations based on your skin color:
- Light skin = 15-20 minutes daily
- Medium Skin = 25-30 minutes daily
- Dark Skin = 40-45 minutes daily
What About Sunscreen?
Sunscreens block the UV rays from the sun, so wearing sunscreen may inhibit your body from producing vitamin D. While it is important to avoid excessive sun exposure, inadequate sun exposure contributes to vitamin D deficiency.
Another important consideration is that many of the sunscreens commercially available contain chemicals that are toxic to the body. A recent study found that the chemicals in sunscreen enter the bloodstream at high levels and remain in the body for at least 24 hours after the use of sunscreen (21). In the study, researchers found that avobenzone, oxybenzone, octocrylene, ecamsule, the active ingredients in sunscreens, were absorbed into systemic circulation at dangerous levels.

Other chemicals commonly found in sunscreens are cinnamates, PABA esters, salicylates, digalloyl trioleate, and menthyl anthranilate. Retinyl palmitate, a form of vitamin A, is also found in many products.
Studies have found that retinyl palmitate may speed the development of skin tumors and lesions (22). Retinyl palmitate and these other chemicals are found in a variety of personal care products with SPF (sun protection factor).
Natural sunscreen protection comes from tropical oils such as coconut, eucalyptus, jojoba, and shea butter. Zinc oxide, when applied appropriately, is a powerful protectant from the damaging effects of too much sun.
You can also prevent carcinogenic activity in your skin before and after sun exposure by using moisturizers like coconut oil, aloe vera, and green tea extract which contain antioxidants. It is also prudent to wear hats and other protective clothing if you know you are going to spend excessive time in the sun.
Here is a great brand of sunscreen that my family uses when we are at the beach or getting a high amount of sun exposure.

Food Sources of Vitamin D
As you can see in the chart below, food is not a great source of vitamin D. With that said, the foods that support your D levels are very healthy foods that supply a rich array of supportive nutrients that are needed for hormone balance and optimizing your vitamin D expression at the cells.
I would encourage you to consume one or more of these top 6 foods every day and certainly at least 7-10 servings per week of them. If you have a food sensitivity to dairy or eggs then consume salmon or other fatty wild-caught fish and mushrooms a few times per week.

1. Salmon and Fatty Fish
Salmon and other fatty fish are good sources of vitamin D. A 3-ounce salmon fillet contains about 450 IUs of vitamin D. It is important when choosing salmon to consume only wild-caught salmon. Farmed salmon is highly toxic.
Wild-caught salmon is rich in the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA which are essential for healthy neurological and cardiovascular function. These fatty acids are also necessary for cellular repair and optimal immune function.
Salmon has the unique antioxidant astaxanthin which gives salmon their pinkish-red color. Astaxanthin has potent anti-aging properties.
Sardines are another excellent source of vitamin D. In fact, a 3.5-ounce can of sardines has around 270 IUs of vitamin D. Sardines also provide omega-3 fatty acids and many vitamins and minerals such as vitamin B-12, calcium, iron, niacin, phosphorus, and potassium.

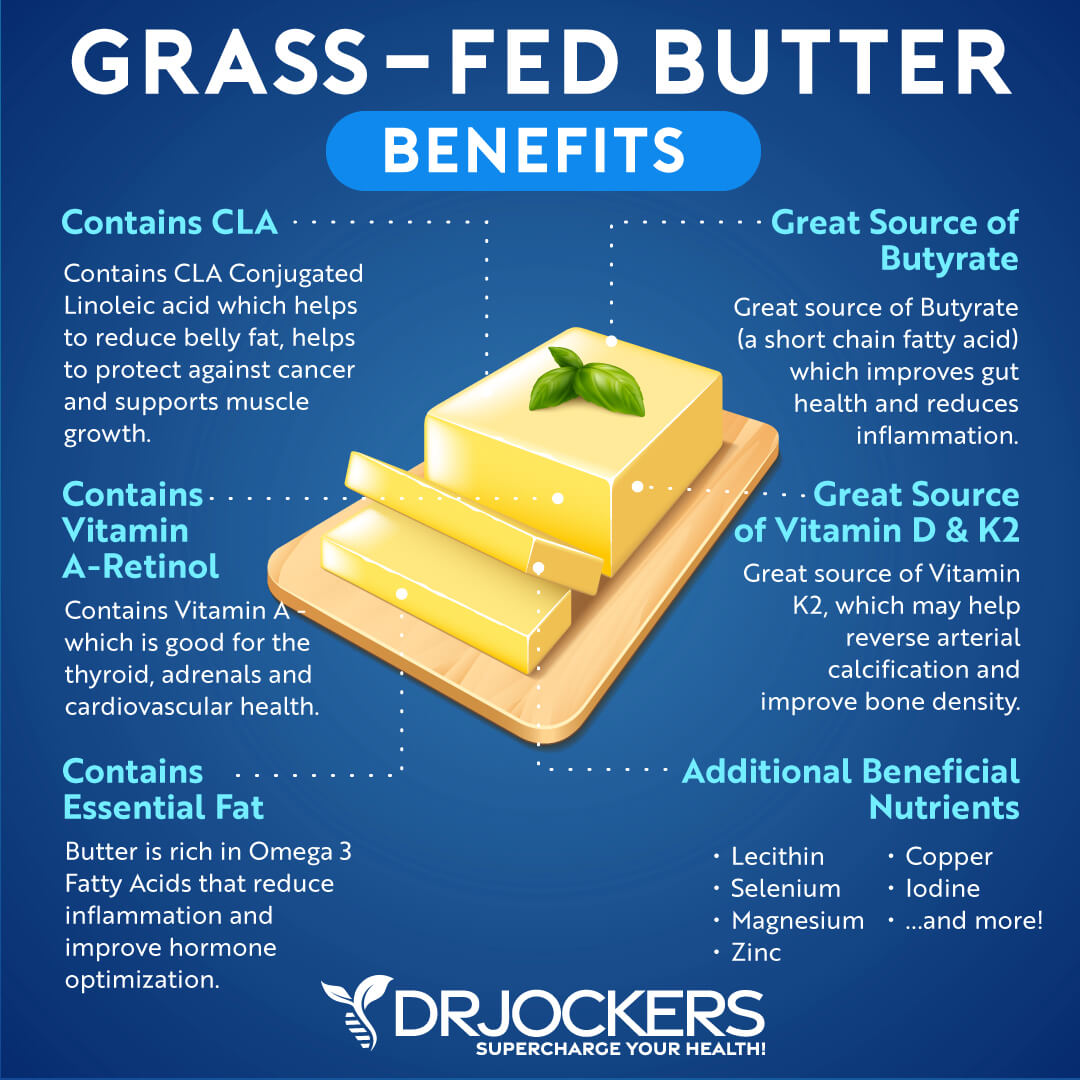
2. Grass-Fed Butter
Grass-fed butter is a delicious source of vitamin D. It is naturally high in omega-3 fatty acids as well as saturated fats and dietary cholesterol which are key for brain health.
Grass-fed butter also contains conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), butyrate, vitamin A, vitamin K2, and other beneficial nutrients. Most people who have trouble with dairy can still do well with butter because it doesn’t contain the protein components whey or casein as well as lactose, which are the typical immune-provoking agents.
3. Raw Grass-Fed Cheese
Raw cheese has the ideal ratio of vitamin K2 and vitamin D3 along with other nutrients that make it the perfect food for healthy bones, joints, and cardiovascular function. It is important to choose raw cheese from grass-fed cows rather than highly processed cheese made from an inferior dairy supply.
Raw cheese from 100% grass-fed cows has the perfect omega 6:3 fatty acid ratio of 2:1. It also contains high amounts of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which is a powerful nutrient that boosts metabolism and enhances natural immunity, along with calcium, magnesium, amino acids, and vitamin A.
4. Egg Yolks
Eggs are one of the most nutrient dense foods on the planet and an excellent source of vitamin D. Vitamin D is only found in the yolk of the egg which contains around 20-40 IUs of vitamin D.
Eggs are a complete protein (6 grams per egg) with a full array of amino acids. In addition to vitamin D, egg yolks are a source of K2 (which works in synergy with vitamin D) zinc, B vitamins, vitamin A, iron, lutein, zeaxanthin, choline, and other nutrients.

5. Mushrooms
Mushrooms produce vitamin D when exposed to ultraviolet light. Most mushrooms are grown in the dark and do not contain vitamin D. Some mushrooms are grown in ultraviolet light to stimulate vitamin D production. Exact amounts of vitamin D depend on the type of mushroom. Chanterelle, morel, shitake or portobello all provide vitamin D.
6. Beef Liver
Organ meats are loaded with powerful nutrition. Beef liver is one of the most nutrient-dense foods available. A 3.5-ounce serving of cooked beef liver contains about 45 IUs of vitamin D. Beef liver contains several other nutrients such as vitamin A, iron, and protein.
If you do not like the taste of liver, you can try this grass-fed, pasture-raised beef liver in supplement form. We have grass-fed beef liver along with beef heart, kidney, pancreas, and spleen in our Grass Fed Beef Organ Complex supplement.
Supplementing with Vitamin D
If you are unable to get a regular amount of high quality sun exposure each week as I described above then you should strongly consider supplementing. The way that I recommend supplementing vitamin D is with a good high quality Cod Liver oil or with specific vitamin D3 supplements that also contain Vitamin K2.
I find Cod Liver Oil a great source for young children as it supplies the omega 3 fatty acids and vitamin A they need as well as the D3 for optimal growth and development of their brain and immune system. For teenagers and adults, you can take a capsule-based or liquid form of D3/K2 supplement.
Cod Liver Oil
Cod Liver Oil is an excellent source of vitamin D. The vitamin D content in cod liver oil is more concentrated than any other food source. One tablespoon contains about 1,300 IUs of vitamin D.
Cod Liver Oil is also an excellent source of the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA along with vitamin A. Vitamin A is required for the synthesis of hormones and is important for the function of the immune system. Because vitamin A is fat soluble, the combination of fatty acids in cod liver oil enhances the delivery of vitamin A to the body.
Many cod liver oils are flavored with mint or citrus to improve the taste. This Cod Liver Oil is lemon-flavored to make it more appealing to children and adults. It also has added vitamin D3 so that each tsp contains 1000 IUs and every tablespoon has 3000 IU’s.
D3/K2 Supplement
Another option for supplementation is using a high-quality vitamin D supplement that also contains vitamin K2. It is important to keep vitamins D3 and K2 in balance. D3/K2 Power has the ideal ratio of these two nutrients. We also have a liposomal form of D3/K2 if you are unable to swallow pills.
It is always best to take vitamin D with other food as it is fat soluble and absorbs best when digestive juices are present. To obtain optimal levels of vitamin D3 through supplementation, we use the following formula:
- To Boost D3/K2 Levels: 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 (35-400 mcg of vitamin K2) for every 25 pounds of body weight. This typically will add 15-20 IU to your blood D3 levels each month. If your levels are 20, supplementing vitamin D using this formula for three months should get the level up to 80. I always recommend that you test your D3 levels to be sure.
- For Maintenance: 1,000 IU of vitamin D3 (15-200 mcg of vitamin K2) for every 25 pounds of body weight Again, be sure to test to make sure!
Testing for Vitamin D Status
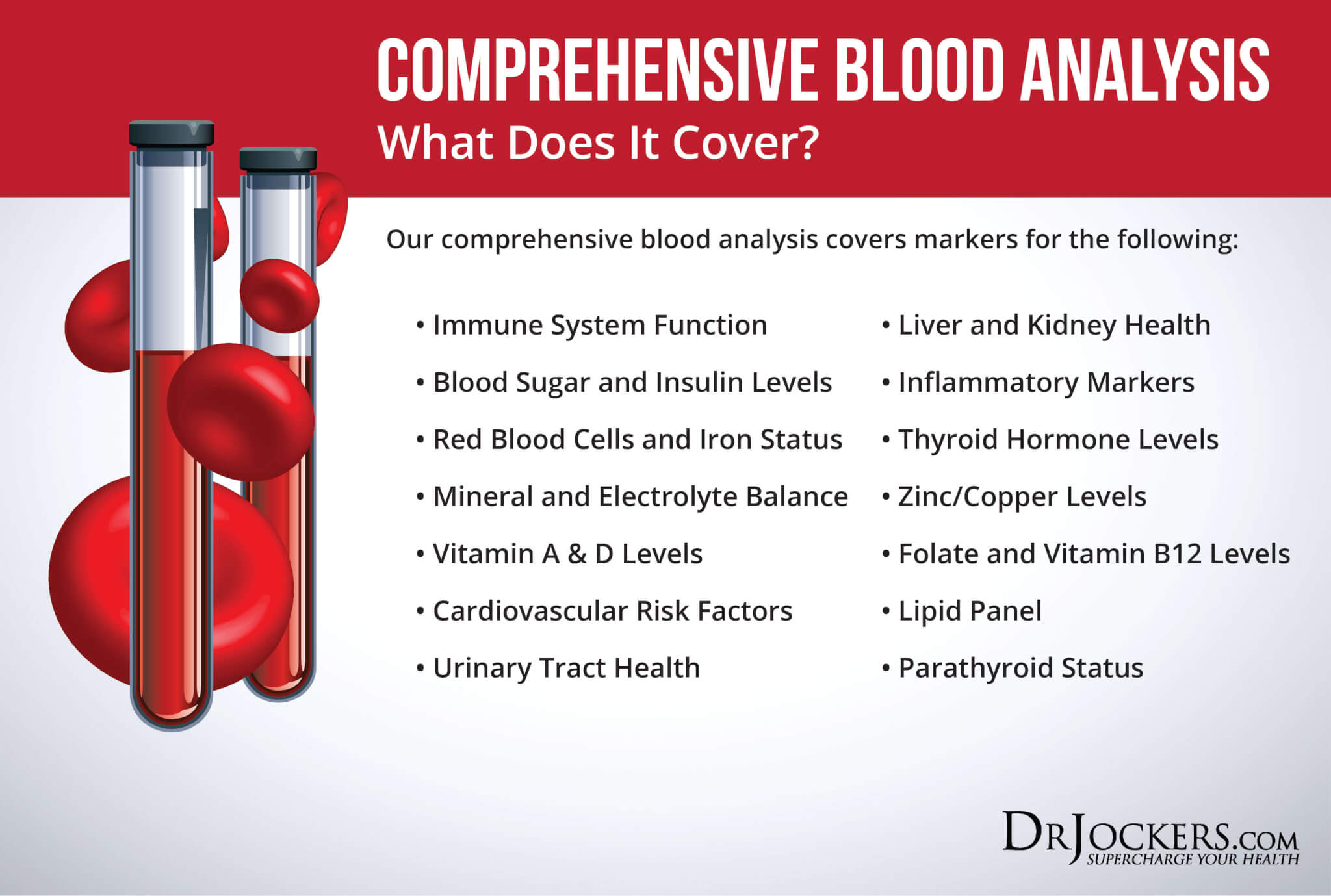
It is very important to test your vitamin D levels. The Comprehensive Blood Analysis is a detailed blood test that includes vitamin D.
The Comprehensive Blood Analysis measures your immune function, thyroid function, blood sugar regulation, liver function, nutritional deficiencies, and much more. It includes a Complete Blood Count, Complete Metabolic Panel, Urinalysis, Lipid Panel, Iron Panel, Inflammatory Markers, Key Nutrient Markers, and full Thyroid Panel.
The Comprehensive Blood Analysis should be run regularly as a preventative measure and to monitor your vitamin D level. Information about the Comprehensive Blood Analysis and how to order can be found here.
Conclusion:
Vitamin D is a critical vitamin for overall health. It helps to boost the immune system, protect the body from cancer, build strong bones, and stimulate autophagy. Vitamin D deficiencies are associated with chronic fatigue, cognitive decline, depression and anxiety, sleep apnea, joint pain, endometriosis, and PCOS.
Unfortunately, vitamin D deficiencies are very common. Around 1 billion people worldwide and 40% of Americans are deficient in this important vitamin.
The sun is the best source of vitamin D. Our bodies produce vitamin D when we are exposed to UV rays. Some foods contain vitamin D such as egg yolks, fatty fish, liver, and grass-fed cheese and butter. Many people do not get enough vitamin D from the sun and foods so supplementation may be necessary.
Be sure to test your level of vitamin D regularly to ensure it is optimal. Maintaining optimal levels of vitamin D is necessary for good overall health and may help to prevent many health issues.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. We do offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out and our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!








I been getting chronic Urinary tract infections could the vitamin D Deficiency cause me to get it
Yes absolutely. A vit D deficiency lowers immunity and makes you more susceptible to infections
My vitamin d was at 111. Is this toxic? Or just a little high?
That is just a little high, but not toxic. If you are taking a vitamin D supplement, I would recommend stopping it for two weeks and then continuing on a slightly lower dosage.