 How Vitamin D Protects Against Respiratory Infections
How Vitamin D Protects Against Respiratory Infections
We’re in the middle of the cold and flu season and we came off 2 years dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic. Protecting your immune system is more important than ever.
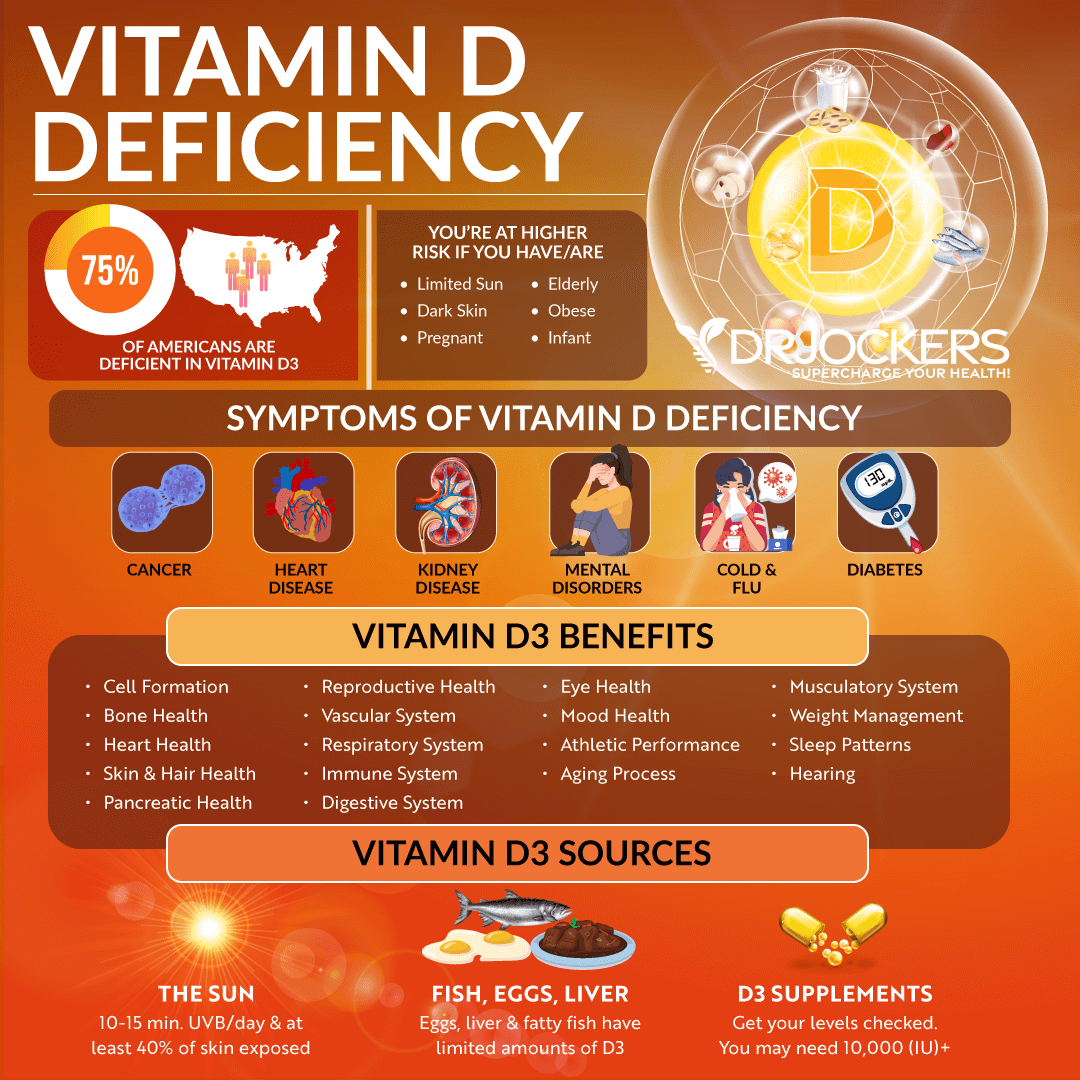
Vitamin D is a key player when it comes to immune protection and your fight against respiratory infections. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that you need for immune function, bone, muscle, brain, and mental health. Even though it’s one of the most vital vitamins, most of our population is deficient in vitamin D. Raising the awareness of the importance of vitamin D and improving your body’s vitamin D levels is more crucial than ever.
In this article, you will learn what vitamin D is. You will understand how vitamin D and your immune function are connected. I will go over the connection between vitamin D levels and viral infections. I will share some studies on vitamin D and COVID-19, as well as, vitamin D and the flu. You will learn about the importance of supplementing with vitamin D and how to do so effectively. I will explain why I recommend testing your vitamin D levels and what are the optimal ranges.
What is Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin your body needs to survive and thrive. It is vital for your immune function, bone and muscle health, brain function, and mental health among other health factors.
When the ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun reach your skin, it triggers vitamin D synthesis in your body. This is the best and ideal way to meet your vitamin D needs. Additionally, there are certain foods that contain vitamin D, including fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel, egg yolks, beef liver, and mushrooms. Eating these foods may improve your vitamin D levels.
However, meeting your vitamin D needs through diet and sunshine alone can be difficult if not impossible. Most of us in the modern world are living a mostly indoor lifestyle and not getting enough sunshine as a result.
If you are living in the Northern part of the United States, Canada, or other parts of the world with gloomy, rainy, or snowy conditions a large portion of the year, meeting your vitamin D needs from the sun alone becomes even more difficult. This makes supplementation with vitamin D critical for most people to obtain optimal vitamin D levels and protect their health.

How Does Vitamin D Work?
When your vitamin D comes from sunshine or food, it will undergo two hydroxylations to get activated and become useful for your body. The first hydroxylation happens inside your liver where vitamin D converts into 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D), or calcidiol.
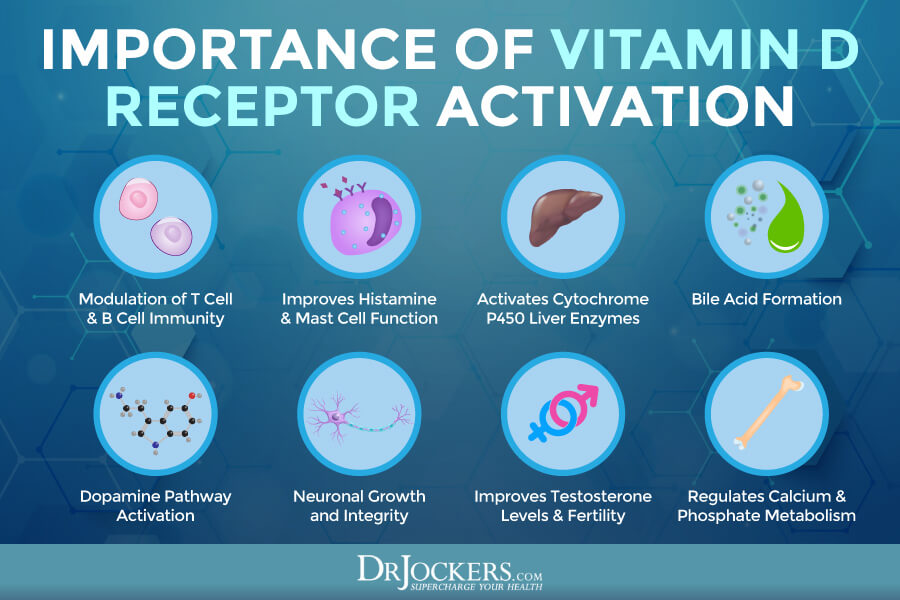
After this, it will go through the second hydroxylation in your kidneys. There it can convert into 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D (1,25(OH)2D), or calcitriol, which is a physiologically active form of vitamin D your body needs that interacts with the VDR receptor on the cells of the body.
This active form of vitamin D is needed for calcium absorption, optimal serum calcium levels, and optimal phosphate concentration. It supports bone growth, bone mineralization, and bone strength. Vitamin D may help reduce the risk of osteoporosis, osteomalacia, muscle spasms, and muscle cramps. It may also support your neuromuscular function, cellular growth, immune health, and cellular metabolism (1).
Vitamin D and Immune Function
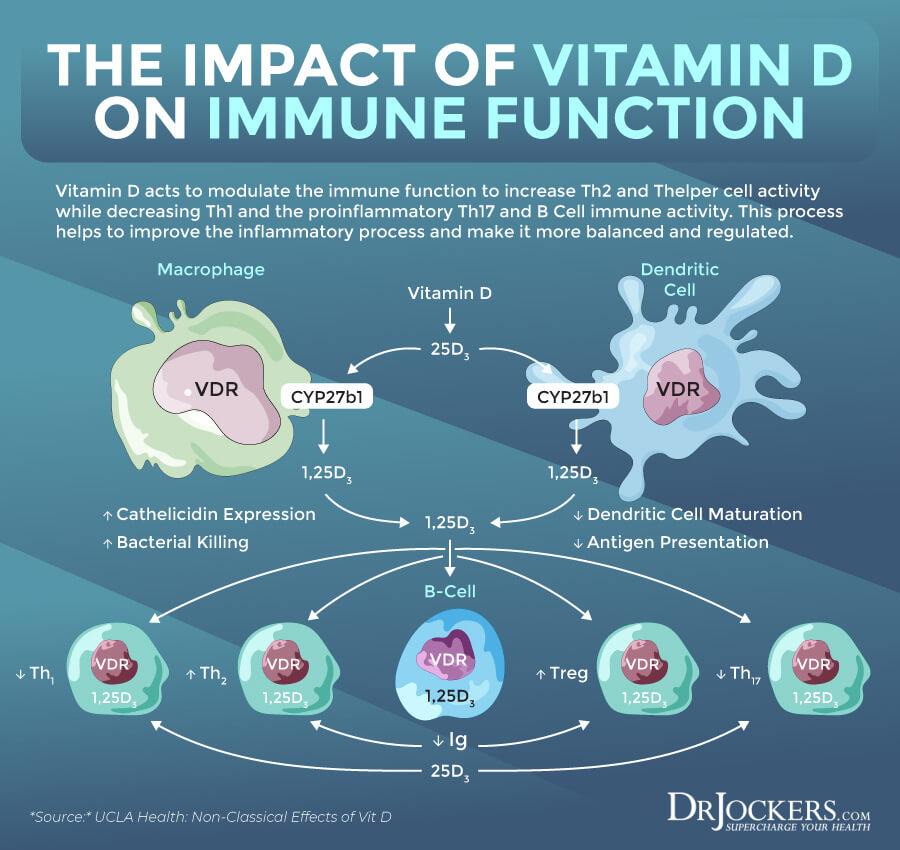
Vitamin D plays an essential role in both your innate and adaptive immune responses. Its active form is critical for maintaining immune homeostasis in your body. According to a 2010 review published in Current Opinion in Pharmacology, vitamin D is an immunomodulator that targets T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes, and various immune cells, such as monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (2). The review has found that vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of chronic infections and autoimmune disorders.
A 2011 book, Vitamins, and Hormones published by the Academic Press has found that the active metabolite of vitamin D, 1,25(OH)2D is an active player when it comes to immune function, immune regulation, and the health of your innate and adaptive immune system (3). Vitamin D deficiency thus may increase the risk and symptoms of immune dysfunction.
Low vitamin D levels may not only increase the risk of autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes or multiple sclerosis (MS), but also increases the risks and outcomes of infectious diseases.
According to the authors of the book, Vitamins and Hormones, vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of tuberculosis (3). Low vitamin D levels may also increase the risk of respiratory infections. For example, according to a 2018 review published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, Vitamin D levels may reduce the risk of viral influenza infections (the flu) (4). Later in this article, you will learn about how vitamin D may play a role in viral infections, such as the flu and COVID-19.
According to a 2011 study published in the Journal of Investigative Medicine, vitamin D receptors are expressed on your immune cells, including your T cells, B cells, and antigen-presenting cells (5). Because of this, vitamin D can influence your innate and adaptive immune response and lower your risk of infections and autoimmune problems.
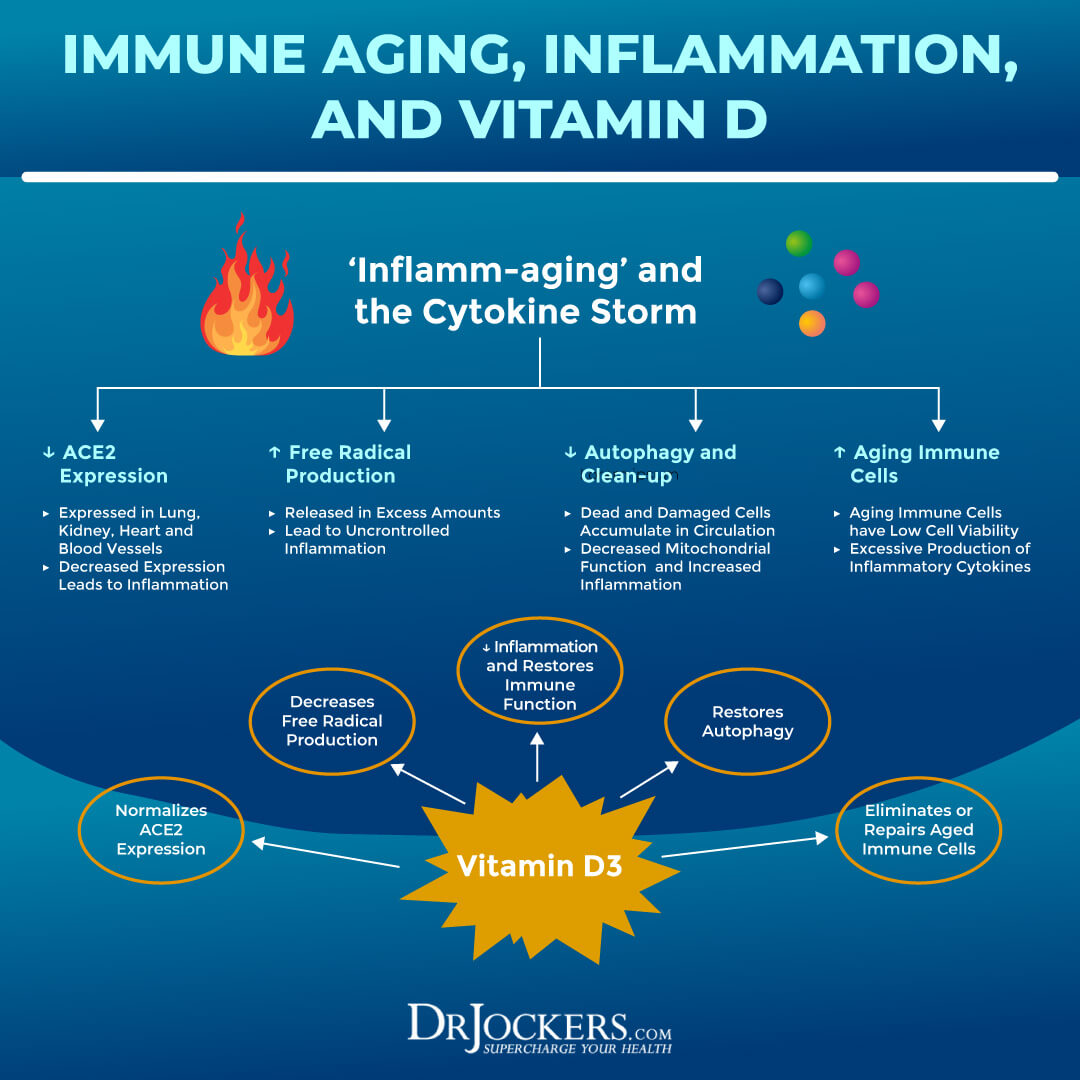
A 2020 study published in JBMR Plus has also found that vitamin D may play an essential role in your immune health (6). According to the researchers, 1,25(OH)2D may increase autophagy in your body. This may support your body in fighting respiratory infections. It can mediate T cell responses, lower inflammation, and even offer antiviral and antibacterial benefits. It turns out that supplementing with vitamin D may support these processes and help to improve your immune health.
Vitamin D and Viral Infections
Vitamin D plays a critical role when it comes to viral infections. It may help to modulate your immune system to stop viral infections, reduce your risks, and support recovery.
A 2019 meta-analysis published in Health Technology Assessment analyzed individual participant data of 10,933 participants and has found that vitamin D supplementation may help to prevent acute respiratory infections (7). A 2020 review published in Nutrients has also found that vitamin D may have immune-modulatory benefits on viral infections (8).
Researchers found that vitamin D deficiency is common among people with viral infections, including influenza, COVID-19, hepatitis, and HIV/AIDS. They found that vitamin D helps to regulate the innate and the adaptive immune system, offer anti-viral properties, and may reduce the risk of infections.
A 2021 article published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition has also found that vitamin D plays a role in immune protection (9). It may help to reduce inflammation, decrease the risk of tissue damage, and may offer an anti-viral immune response. Researchers suggested that vitamin D may be beneficial for those with COVID-19 as deficiencies in vitamin D have been linked to increased risk of severe disease and mortality.
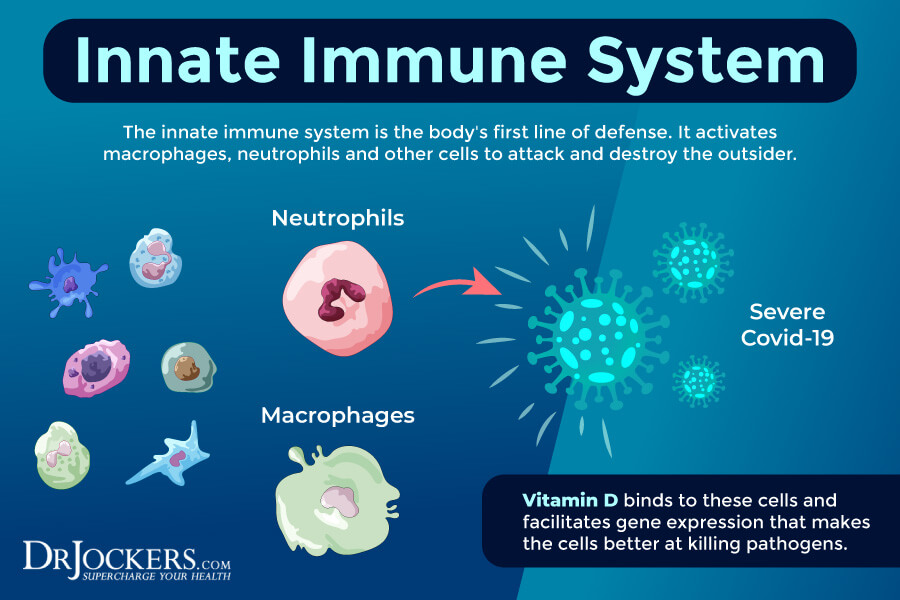
Studies on Vitamin D and COVID-19
You’ve probably seen blogs and social media posts floating around on the potential benefits of vitamin D and COVID-19. There is a good reason for that. There is a good number of research evidence that suggests that vitamin D is important when it comes to supporting your body during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A 2021 systematic review and meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Public Health has also found that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to an increased risk of COVID-19 infection and adequate levels reduced the risk (10). Looking through 318 studies on vitamin D and COVID-19 and selecting 14 that met the inclusion criteria, researchers found that people with vitamin D deficiency were 80 percent more likely to get infected with COVID-19.
A 2021 systematic review published in Frontiers in Public Health has looked at 49 printed and 5 pre-print publications and a total of 1,403,715 cases on the relationship between vitamin D deficiency, COVId-19 infections, related hospitalization, and mortality. The review has found that patients with low vitamin D levels had an increased risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and mortality from COVID-19 (11).
A 2021 meta-analysis of observational studies published in the Journal of American College of Nutrition has looked at 3637 participants to better understand the connection between vitamin D and COVID-19. Similar to other research, they also found that vitamin D deficiency has increased the risk of serious disease and mortality in COVID-19 (12). Patients with low vitamin D levels were more likely to have hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or other risk factors.

Studies on Vitamin D and Flu
The flu has clearly been around for longer than COVID-19. Every year, we deal with the flu season, so it’s important that you protect your immune system year-round to support your body through this period. The effects of vitamin D on the flu virus has been studied for decades, the following studies are just a few examples.
A 2018 multicenter, randomized, open, controlled clinical trial published in The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal has found that vitamin D may reduce the risk of season influenza A in infants (13). Researchers looked at 400 infants during the study and broke them into low- and high-dose vitamin D groups.
Out of the 121 total cases, 78 were in the low-dose and 43 were in the high-dose vitamin D group. The symptoms of those infants in the high-dose group also resolved quicker than in the low-dose one. The results suggest that a higher dose (1,200 IU in this case) of vitamin D may help to reduce the risk and improve recovery of the flu during infancy.

A 2020 review published in Nutrients has found that vitamin D may reduce the risk of respiratory infection, serious illness, and death in both influenza (the flu) and COVID-19 (14). According to the review, vitamin D may decrease the concentration of inflammatory cytokines and as a result may lower the risk of lung infections, pneumonia, and ARDS.
Researchers found that vitamin D deficiencies in common in chronic diseases and health issues that increase the risk of complications for the flu and COVID-19. The authors of the review recommend 10,000 IU/dL of vitamin D during the initial phase of the infection followed by 5,000 IU/dL after a few weeks with a goal to achieve 40 – 60 ng/mL 25(OH)D.
A 2021 paper published in the Economics and Human Biology has found that sunlight, which increases vitamin D production and vitamin D levels, may reduce the risk of the flu (15). Researchers found that the relationship between sunlight and influenza respiratory infections was one of the main driving factors during the H1N1 epidemic in 2009.
They found that about a 10 percent rise in relative sunlight has reduced the influenza index by 1.1 points on a 10-point scale. These results corresponded with the number of flu cases in various counties in New York State. This suggests that beyond supplementation with vitamin D, simply spending time on the sun may help to reduce risk.
Using Vitamin D Supplementation for COVID-19
Looking at the research evidence, you are probably not surprised when I say that using vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 may be a great support strategy. Let’s look at some research evidence before I get into how to use vitamin D supplementation.
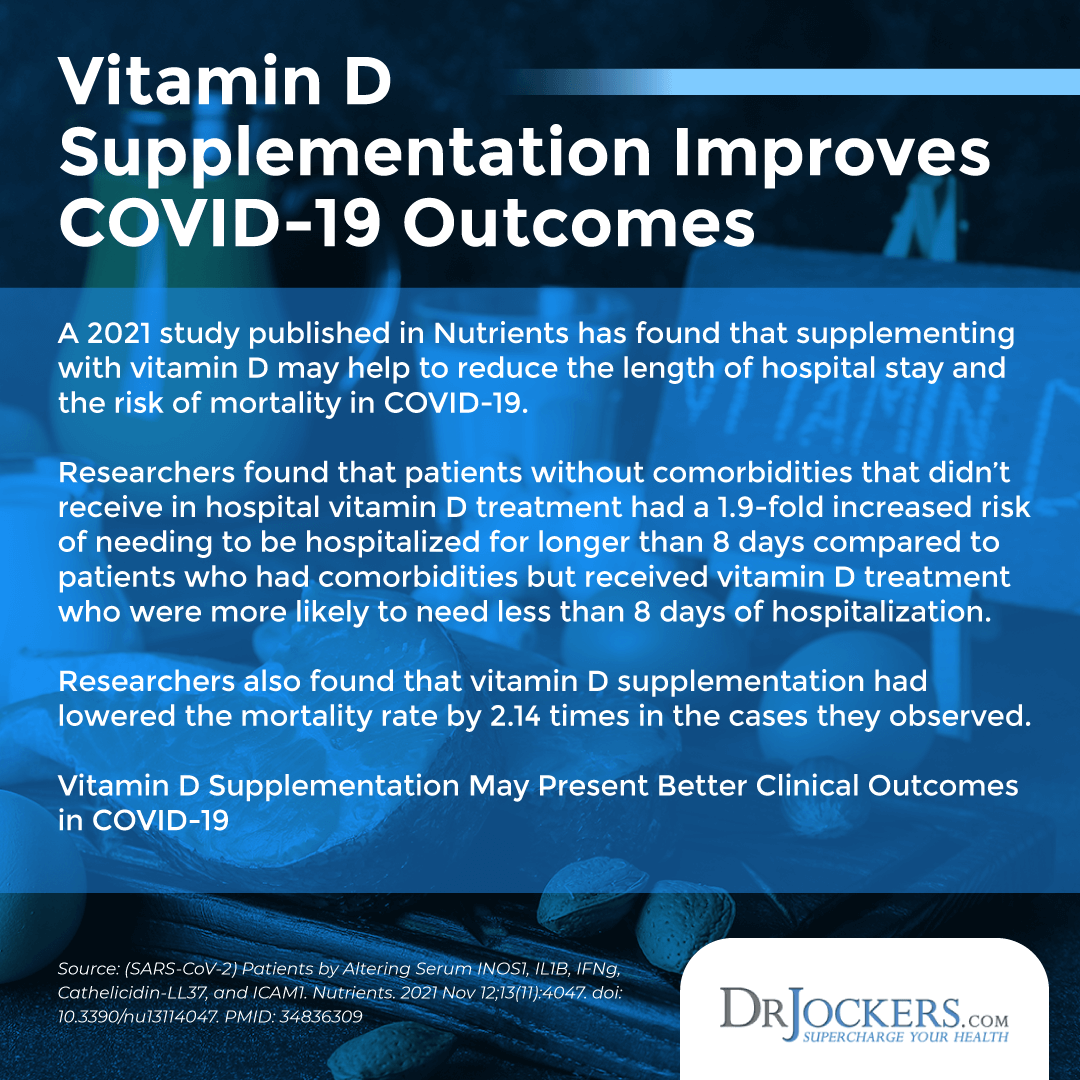
A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that supplementing with vitamin D may help to reduce the length of hospital stay and the risk of mortality in COVID-19 (16). After analyzing the past data of 867 COVID-19 cases, researchers conducted a prospective study with 23 health individuals and 210 cases. 163 of the cases received vitamin D supplementation. The results suggest that vitamin D supplementation has helped to increase the vitamin D levels of patients and raise it above 30 ng/mL only within two weeks.
Some patients had existing comorbidities or health issues that may increase their risk of serious illness, hospitalization, and mortality. Researchers found that patients without comorbidities that didn’t receive vitamin D treatment had a 1.9-fold increased risk of needing to be hospitalized for longer than 8 days compared to patients who had comorbidities but received vitamin D treatment who were more likely to need less than 8 days of hospitalization.
This suggests that adequate vitamin D levels and vitamin D supplementation may be important for those who don’t have any existing health risk factors. Researchers also found that vitamin D supplementation had lowered the mortality rate by 2.14 times in the cases they observed.
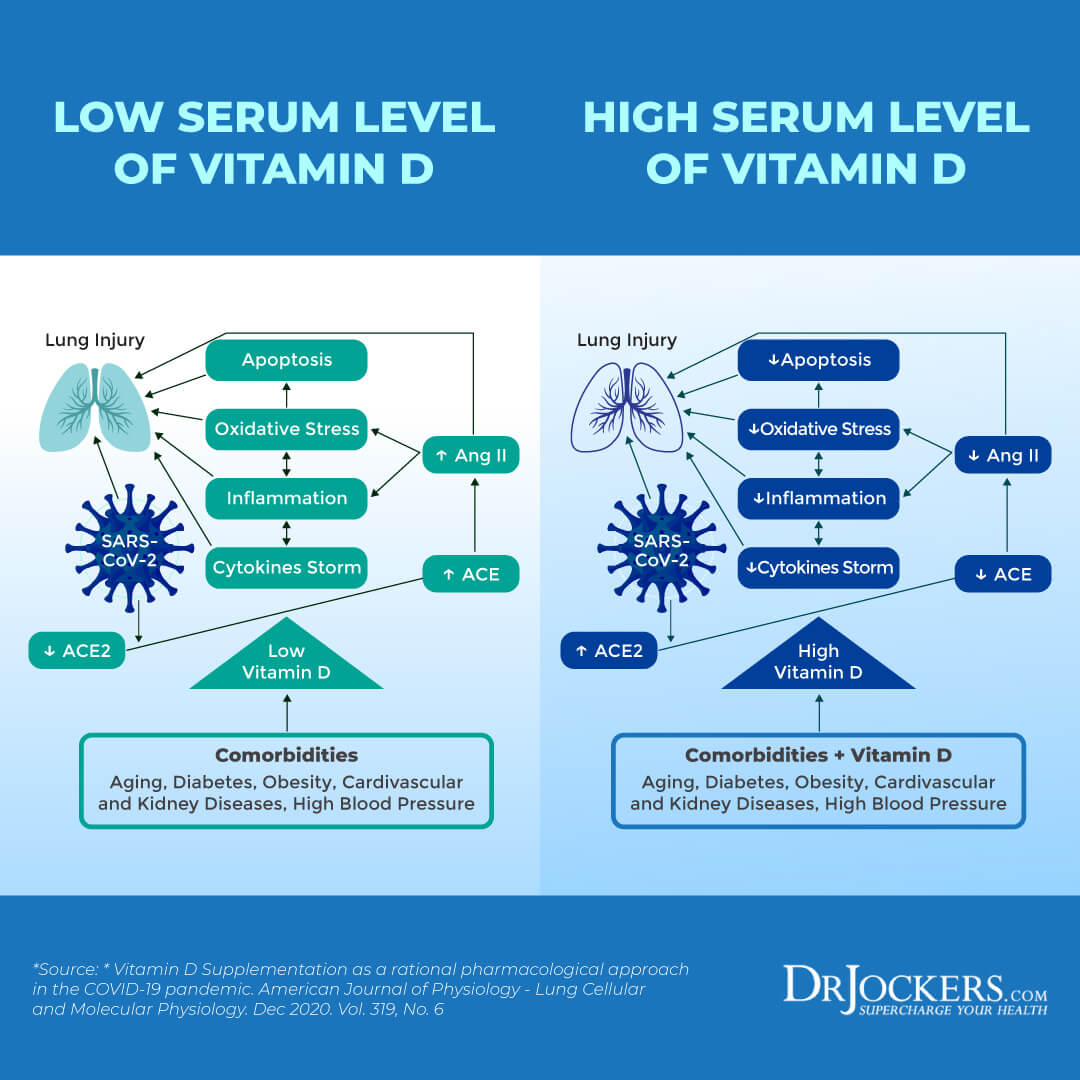
Vitamin D and Respiratory Infections
A population-cohort study published in 2022 in the Journal of Endocrinological Investigation has also found that vitamin D supplementation may improve COVID-19 outcomes (17). The study looked at COVID-19 cases of individuals who supplemented with vitamin D between April 2019 and February 2020 and compared them to a control group who did not. Researchers looked at the difference between how they faired during the first wave of the pandemic in 2020.
They found that patients who supplemented with cholecalciferol had a reduced risk of COVID-19 infection. Those who achieved at least 30 ng/mL 25OHD levels through cholecalciferol supplementation experienced a reduced risk of infection, severe disease, hospitalization, and mortality compared to the control group.
Researchers found that though calcifediol supplementation alone didn’t reduce the risk of COVID-19, those who achieved at least 30 ng/mL 25OHD levels through calcifediol supplementation did have a lower risk of respiratory infection, severe disease, hospitalization, and mortality from COVID-19. Researchers found that the key to decreasing the risk of COVID-19 infections and associated severe illness, hospitalization, and mortality may lie in having at least 30 ng/mL 25OHD.

Testing Vitamin D Levels
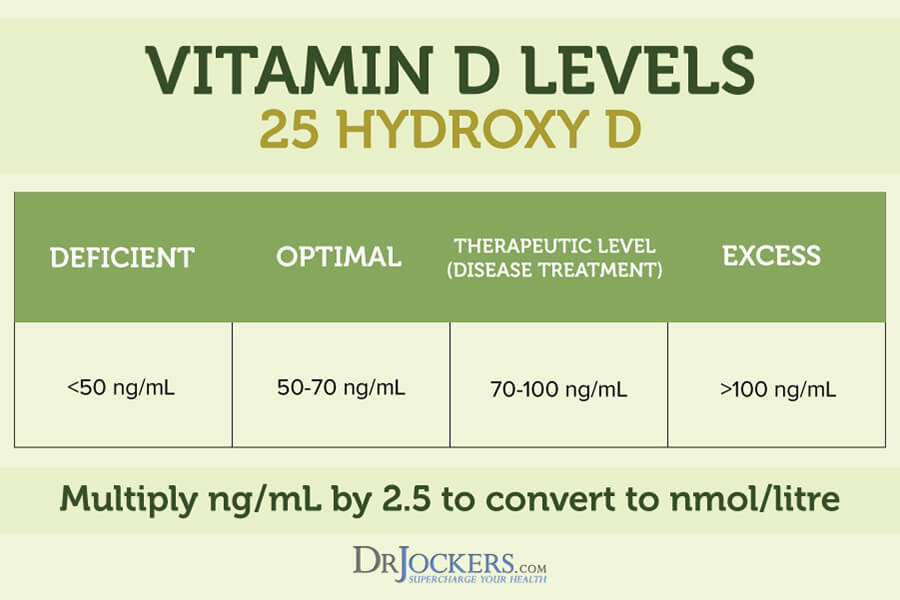
I recommend testing your vitamin D levels to see if you are dealing with deficiency and immune health risks. Testing can help us determine the best supplementation strategy for you. When it comes to vitamin D levels, most studies use <20 nmol/L for very deficient, <30 nmol/L for deficient and >30 nmol/L for normal vitamin D levels. However, simply being a bit over 30 nmol/L is far from enough. Optimal levels of vitamin D are over 50 nmol/L and this is what we are aiming for in functional medicine.
When analyzing your vitamin D levels, I also recommend that we look at your 1,25-OH Calcitriol and 25-OH cholecalciferol D3 levels to understand the full picture. Optimal ranges for 1,25 OH Calcitriol is between 50 and 100 ng/ml and for 25-OH vitamin D3 it is also between 50 and 100 ng/ml.
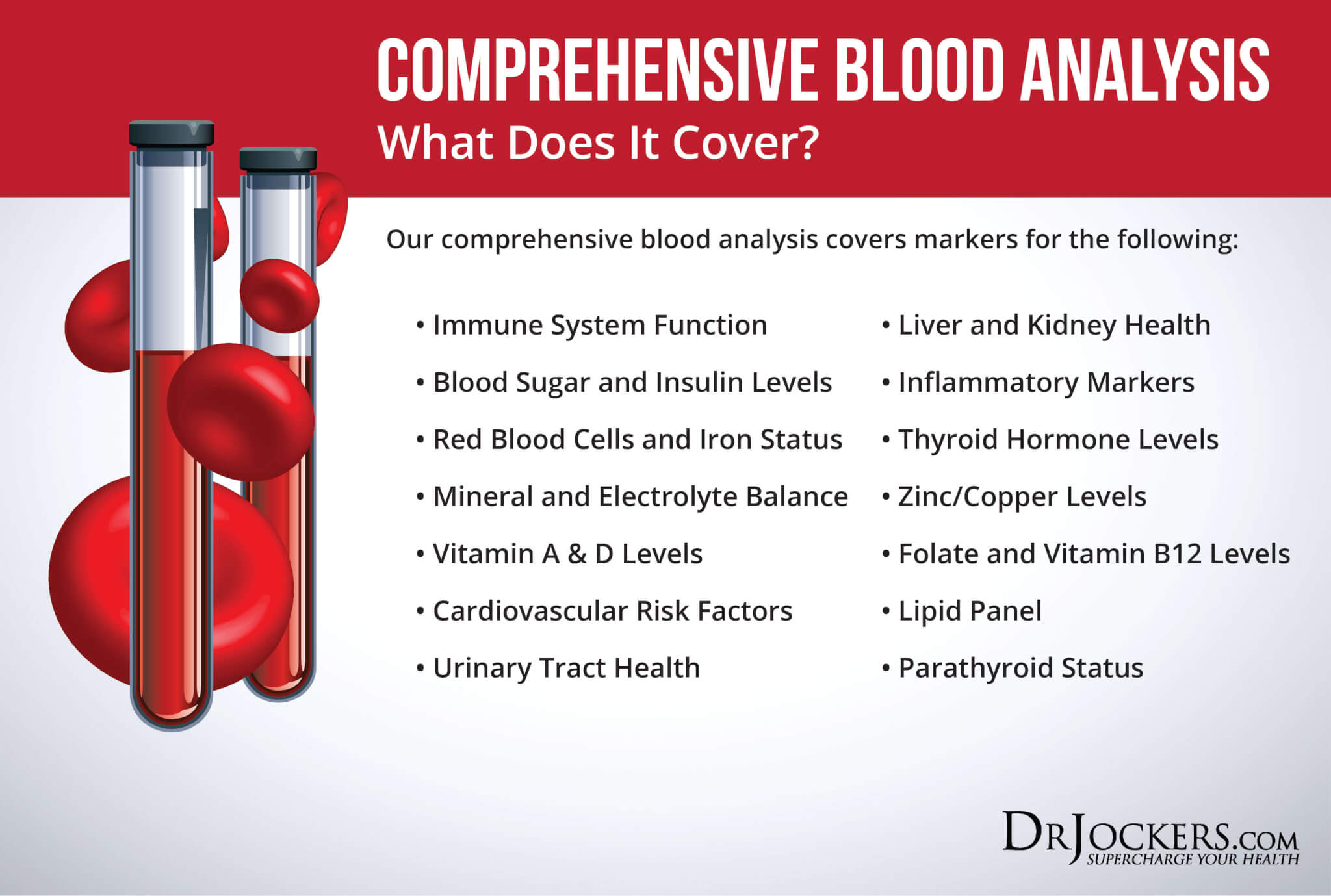
Comprehensive Blood Analysis
I recommend a Comprehensive Blood Analysis (CBA). This test is more sophisticated than most conventional doctors are able to order. With the help of this test, we are able to look at your 25(OH) and 1,25(OH). For some individuals, they struggle with vitamin D resistance where they are unable to increase their vitamin D levels in spite of supplementation.
For these individuals, we have to look at a wide variety of markers including inflammatory markers, parathyroid function, calcium and magnesium levels, liver markers and more. This is where the CBA is so helpful, because it looks at inflammatory markers, vitamin A, PTH, calcium, magnesium, complete metabolic panel, complete blood count, liver function markers, blood sugar levels, nutrient deficiencies, and more. I recommend getting the CBA done regularly both as a preventative measure and to monitor your progress.
Final Thoughts
Vitamin D is one of the most vital vitamins and is critical for immune health and fighting respiratory infections, most of our population is deficient in vitamin D. Raising the awareness of the importance of vitamin D and improving your body’s vitamin D levels is more crucial than ever.
I recommend that you follow my tips and start supplementing with vitamin D to support your immune health and protect your health against respiratory infections. For more information on addressing vitamin D levels, read this article here.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. On our website, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!




My Dr goes ballistic to see my vitamin D levels over 130 (lab tests no higher #’s than 130). But I take more than adequate amnts of K2/MK7, incl sauerkraut. What’s amenable D levels w/MK7 in the mix? I’m disappointed that I can’t find medical research on this.
Hello Duane, I think you are totally fine and perhaps even more healthy with vitamin D levels up to 150 ng/mL as long as you are also sufficient in magnesium, vitamin A and vitamin K2.
Hi Dr. Jockers,
is it important to take K2 with D3 or would be enough D3 by itself and consuming green-leaf veg and Cabbage?
Lately I was wondering why a good brand Global Healing have not K2 with their D3.
I would like to know your thoughts! Thank You!
Hi Doc. I calculated my D3 dosage by multiplying my wt. in lbs. x desired lab level, which was 100ng/ml. I’m 180 lbs, so 180 x 100 is 18,000 iu daily. I take 20,000 daily, so expected a 111ng/ml lab level. 3 months later, level was 113. Pretty accurate. I feel this level is effective and safe, as the 2023, 7-yr, 4,000 pt., Ohio study reported an avg 118ng/ml with no hypercalcemia or side effects, and great health outcomes. The study used the sun providing 25,000 iu daily as the standard. 5,000-50,000 iu daily were provided, as well as a placebo group. Dr. John Campbell dissects the study well on YouTube, entitled “Vitamin D Doses”. The NIH has also posted the study. Thanks for your platform. Your Lipo C report is incredible, btw.