Understanding the Role of Methylation
Methylation is a critical process that happens trillions of times in every cell each minute. It is one of the most essential metabolic functions of the body and is dependent upon a variety of enzymes. Adapting to stress and the challenges of life is an aspect that methylation provides the body. Without adequate methylation processes the individual cannot adapt effectively and will suffer the deleterious effects of accelerated aging (1).
Methylation is a controlled transfer of a methyl group (one carbon and three hydrogen atoms) onto proteins, amino acids, enzymes and DNA in every cell and tissue of the body to regulate healing, cell energy, genetic expression of DNA, liver detoxification, immunity and neurology.

Inadequate Methylation Symptoms:
Cardiovascular Disease (2) Diabetes (3)
Multiple Sclerosis (4) Psychiatric Disorders (5)
Chronic Inflammation (6) NeuroTransmitter Imbalances (7)
Abnormal Immune Function (8) Dementia (9)
Autism (10) Fertility & Miscarriages (11)
Cancer (12) Chronic Fatigue (13)
Alzheimers (14) Down’s Syndrome (15)
Pregnancy Problems (16)

Why is Methylation Important for Health?
Methylation is involved in almost every bodily biochemical reaction, and occurs billions of times every second in our cells. That’s why figuring out where there are challenges in the cycle and how to help it perform better will significantly improve our health.
There are many key functions of methylation, for example methylation is intimately involved in all of the following processes:
Turn on and off genes (gene regulation) – this is important in cancer for example (17)
Process chemicals and toxins (bio transformation) helping to reduce our toxic load (18)
Builds neurotransmitters (dopamine, serotonin, epinephrine) (19)
Processes and metabolizes hormones (estrogen) (20)
Build immune cells (T cells and NK cells) (21)
Synthesis of DNA and RNA (thymine is formed from uracil) (22)
Produce energy (CoQ10, Carnitine and ATP) (23)
Produce protective coating on our nerves (via myelination) (24)
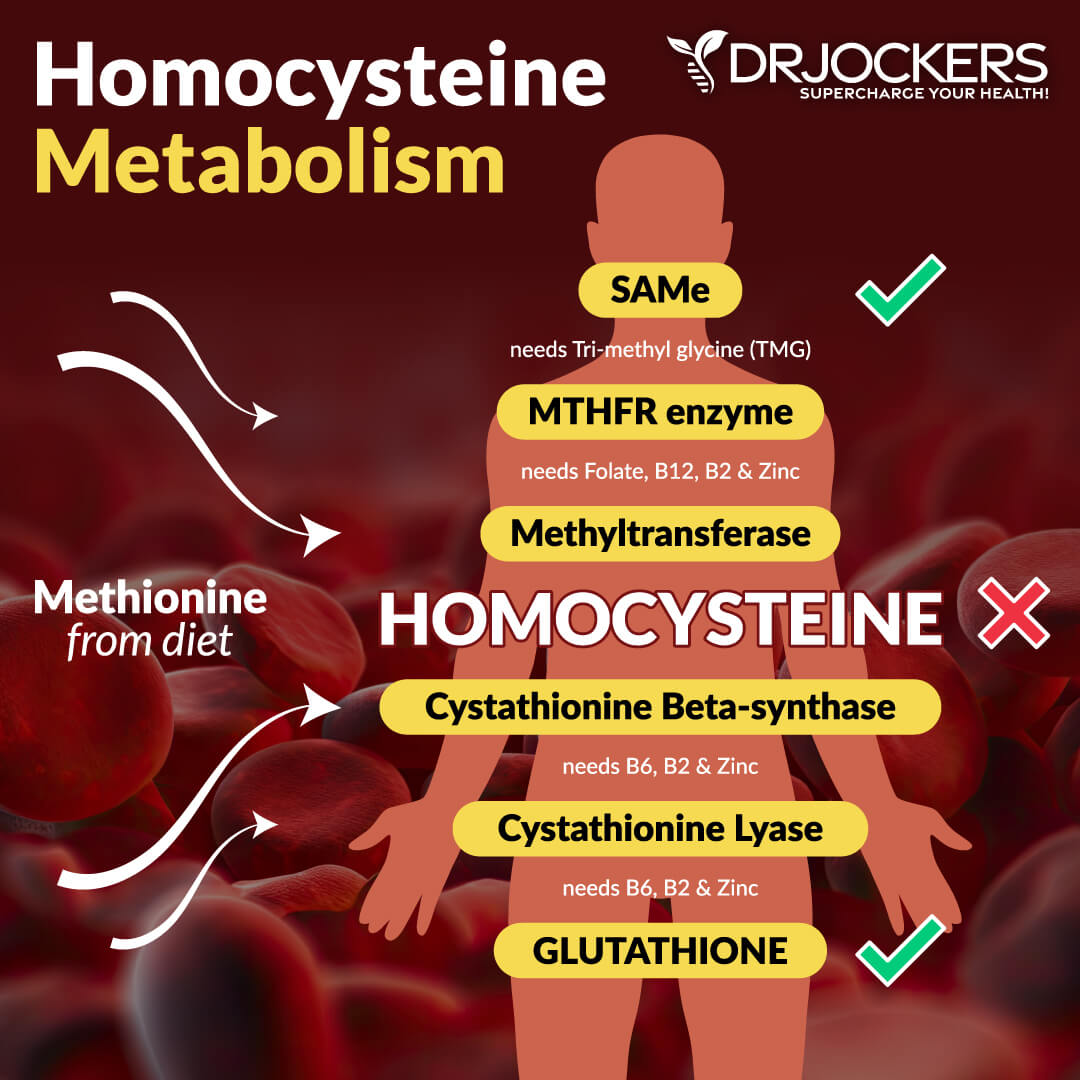
Elevated Homocysteine Levels:
Homocysteine is a metabolic byproduct of protein metabolism and in particular the metabolism of methionine. Methionine is found in meats, seafood, dairy products, eggs, sesame seeds and Brazil nuts.
Homocysteine is metabolized through two pathways: remethylation and transsulfuration. Remethylation requires folate and B12 coenzymes while transsulfuration requires pyridoxal-5-phosphate, the B6 coenzyme.
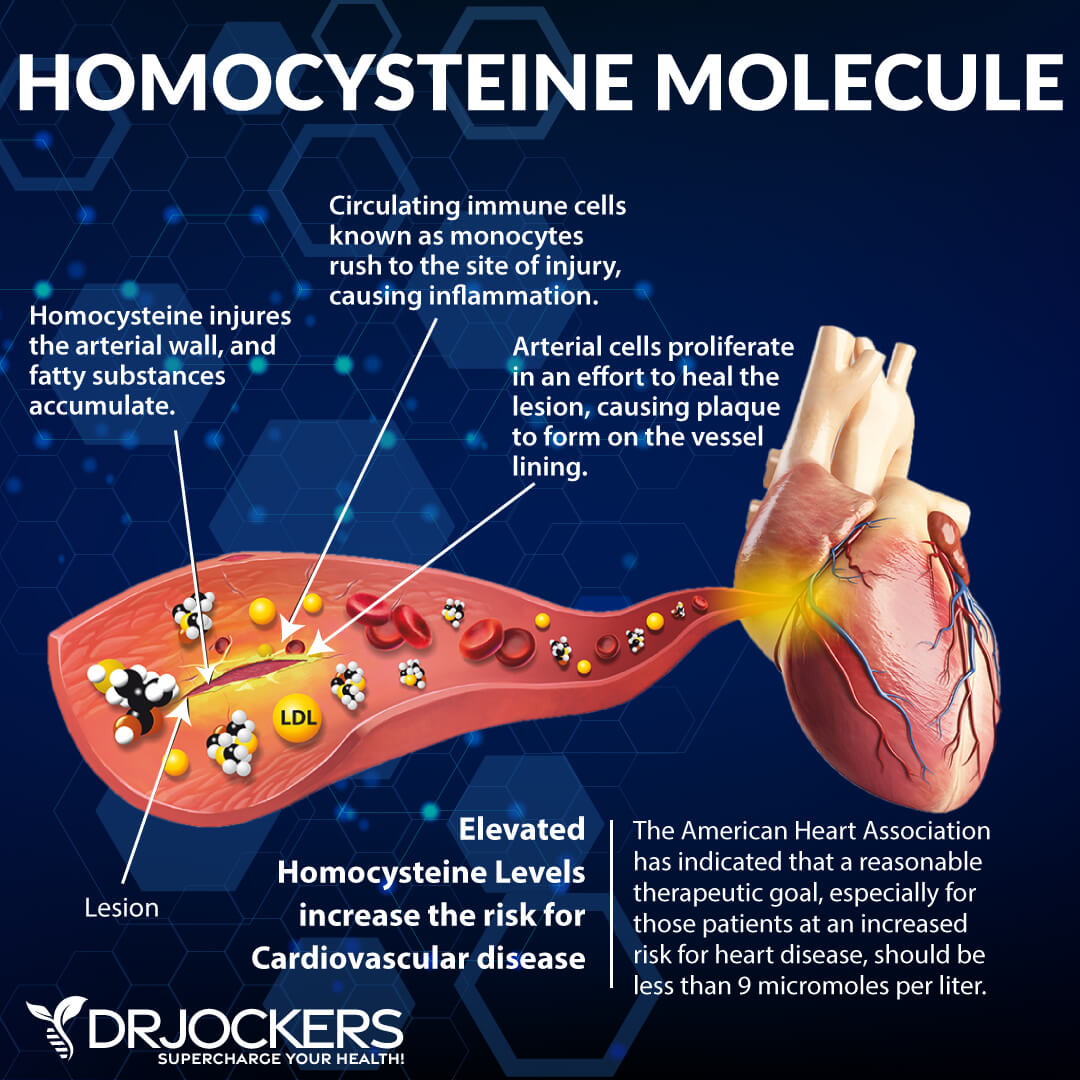
Control Homocysteine Levels
Elevated homocysteine causes excessive clotting which diminishes blood flow to major regions of the body. The lack of blood supply to the heart may cause heart attacks and the lack of blood supply to the brain accelerates the development of dementia and may lead to strokes.
High homocysteine is also associated with blood clots in other major regions of the body. This includes the veins in such conditions as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. In some studies, even moderate levels of homocysteine levels showed higher rates of incidence of blood clot formation

What Influences the Methylation Process?
Methylation is regulated by key enzymes and cofactors for activation (25). This process is dependent upon certain vitamins and minerals. When we are deficient in the necessary substrates and cofactors it compromises the methylation processes.
There are many key nutrients that play a role in methylation. These include zinc, magnesium, B2, B6, folate, B12, niacin and others (26). Many people consume diets that are deficient or deplete their bodies of these key nutrients. Other individuals have genetic polymorphisms that reduce their ability to absorb and utilize these nutrients (27).
Medications such as birth control pills, NSAID’s and antacids deplete these nutrients and consume massive quantities of methyl groups for proper detoxification. Heavy metal exposure, chronic infections, alcohol consumption and heavy emotional stress also deplete methyl groups and put us at risk (28, 29).

Testing for Methylation Imbalances:
Methylation imbalances are often not considered by most doctors and health coaches. Most health care practitioners and health coaches have little to no education in methylation. Those who are well educated in this subject are the premium when it comes to getting to the underlying cause of your health problems.
Specific blood work can evaluate the plasma levels of methionine, cysteine, SAMe, SAH, Homocysteine and cystathione. These tests also give the important “methylation index” (ratio of SAMe to SAH). The results of this test can guide the nutritional support to improve methionine metabolism, reducing homocysteine and the consequences of inadequate methylation and transsulfuration capacity (30).
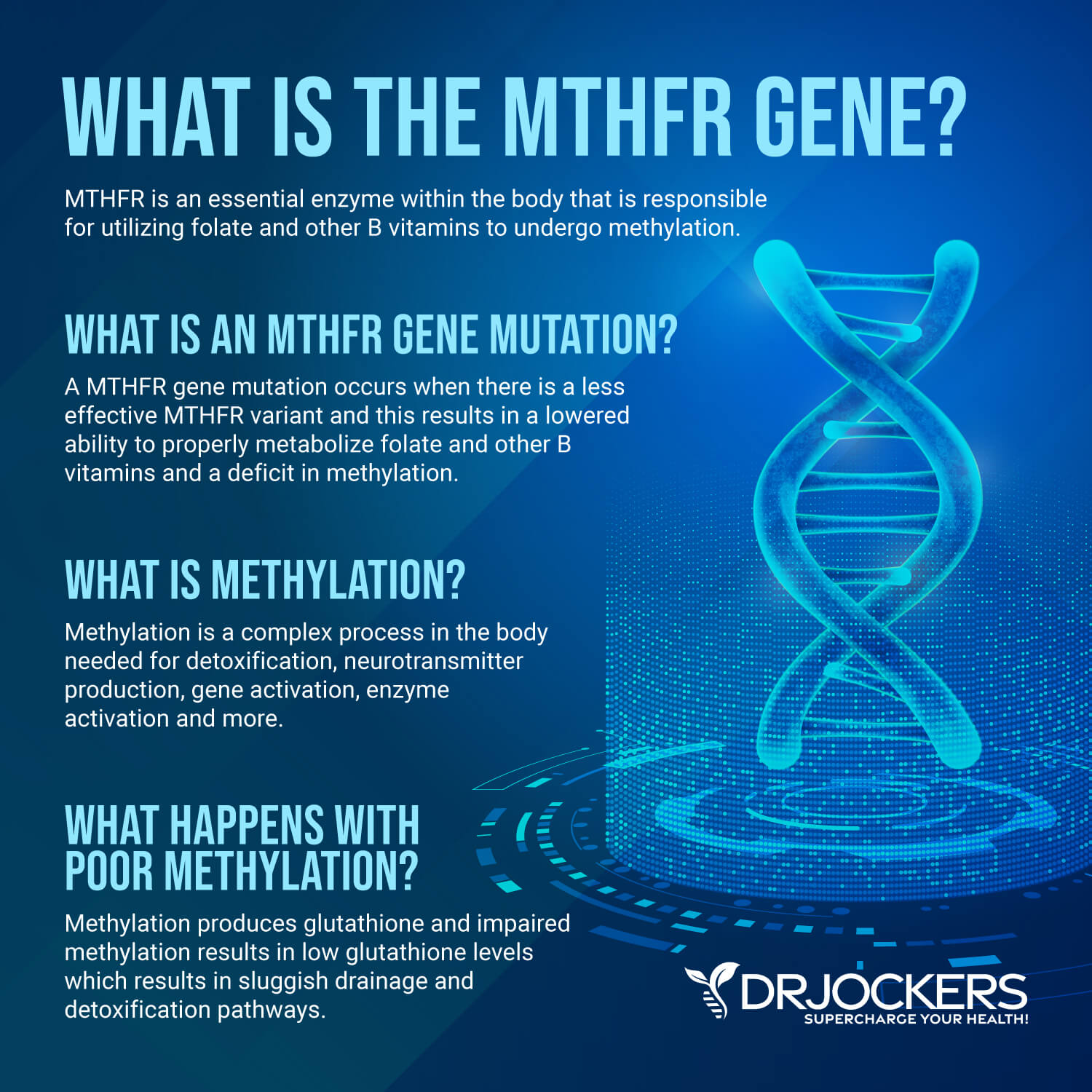
Genetic Influences and on Methylation:
Genetic variations play a very important role in the methylation process. The presence of SNP (single nucleotide polymorphisms) is often a major factor in identifying the underlying cause of imbalanced methylation. A SNP may be present in one or both of the genes. When it is present on one of the genes it is called a heterozygous polymorphism and when it is on both of the genes it is a homozygous polymorphism.
Every part of the methylation pathway can be influenced by SNP’s. The most popular and well-studied one is MTHFR or methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. This enzyme converts 5,10 methylene Tetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5 methyl THF). 5-methyl THF then passes its methyl group to hydroxyl-B12. Hydroxy-B12 then becomes methyl B12 by methylating homocysteine. This process converts a potentially dangerous substance (homocysteine) into a very important molecule called SAMe.

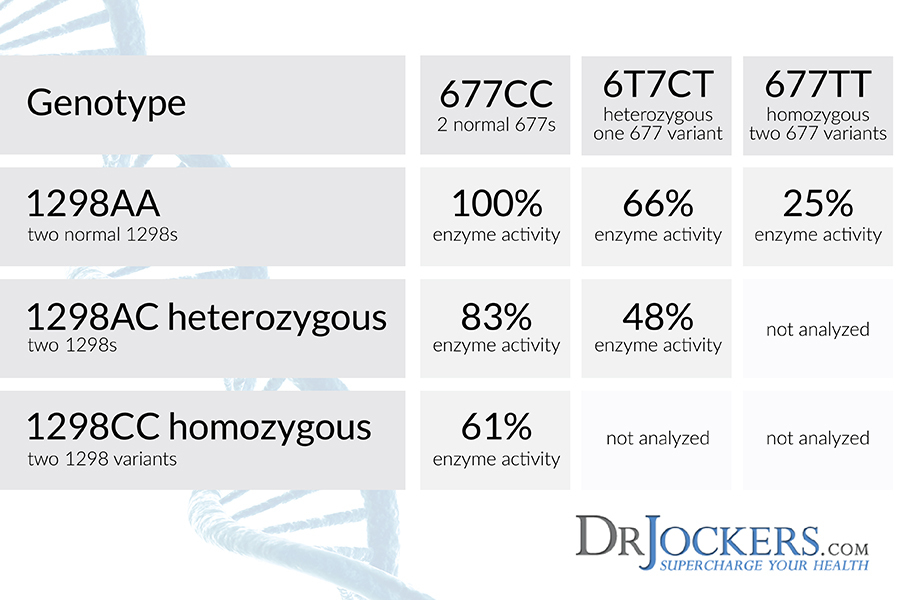
MTHFR Polymorphisms:
There are two key MTHFR polymorphisms – A1298C and C677T. The effect these have on the methylation cycle and overall health are different between the two. C677T SNP’s are associated with elevated homocysteine levels (31). Elevated homocysteine is a major risk factor for heart disease and neurodegenerative states such as Alzheimer’s disease (32, 33).
A1298C SNP’s do not lead to elevated homocysteine but instead play an important role in neurotransmitter function. The 1298C is important in the conversion of BH2 to BH4 which plays a huge role in mood regulation and addictive behavior (34).
Nutrigenomics and 21st Century Health
The field of Nutrigenomics or the science of how nutrition interacts with our genes is revolutionizing our understanding of how to apply specific supplementation to meet an individual’s needs. As we continue to develop our understanding of these SNP’s and the methylation cycle we will be even better at addressing the underlying cause of variant health issues.
Epigenetics is a term that is used to identify how the environment interacts with our genes. Epigenetic research has shown that our environment can change our genetic structure far beyond what we inherited from our parents. Our lifestyle habits, environmental conditions and toxic exposure can change our genes to the point where those changes are passed onto our offspring (35).
One supplement that I use for special cases in need of methylation is Methyl Power. Check it out here
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!





Tests show I’m a low methylator…so, I take 2 balanced B’s to help speed up detox. Since i increased the B’s, I feel unwell: nauseous and frequent BMs…and of course, as you know I have adrenal fatigue to deal with, and am on an SSRI. My question is: is there a link between detoxing and feeling lousy?
Hi Robyn- Yes, what you are referring to is a healing crisis. I would recommend you find a functional health practitioner to customize a specific plan for if you aren’t working with someone yet. Here is a helpful article: https://drjockers.com/functional-nutrition-tips-to-find-a-great-health-coach/. Also read this article for more information on healing crisis: https://drjockers.com/experiencing-healing-crisis/
Sorry, but I had another question: how long does it take to methylate a lifetime of toxins?
Your valued opinion, pls..
Hello, Dr. J.
I had a question about your Methyl Power. Would you pls be good enough to tell me how many mcg or mg of each B vitamin is in it. I want to compare to the one i take.
Thanks a lot!
R:-)
Sure thing Robyn! 25 mg Riboflavin, 10 mg Vitamin B6, 2000 mcg Folate, 1000 mcg Vitamin B12 and it also contains 500 mg Betaine Anhydrous.
Thanks a lot, Dr. J…i’m taking Advanced B Complex by AOR…have you heard of it? If you want to check it out…it’s got methylcobalamin.
Thanks Robyn!
Hi Dr Jockers,
I’ve heard that taking folic acid can mask a B12 deficiency and make it worse.
So shouldn’t we all test first for vitamin B12 deficiency, correct it if present and then supplement the other B vitamins?
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Optic Neuropathy: a Teaching Case Report
https://journal.opted.org/article/vitamin-b12-deficiency-optic-neuropathy-a-teaching-case-report/
Thank you for your time!
Yes Natalia, and this is why I am a huge fan of testing for B12 and I only advise giving folate in combination with other methylation nutrients such as methyl-B12, B6 (P-5-P) and B2.
Thank you for the answer
Dr. Jockers! I am a huge fan of your work and appreciate the information you provide 🙂
We all should be careful when taking supplements… I’ve also read that taking too much
vitamin B2 (riboflavin) can cause eyefloaters in some people
because it is a
retinal photosensitizer…
For this reason, I believe that we as patients should avoid taking more than five times the recommended daily allowance of B2 and limit the exposure to light when taking them.
Keep up with your great work!
Thanks for sharing Natalia!
Dr. Jockers,
I am positive for compound heterozygous for C677T and A1298C. My vitamin b6 has been very high, but other vitamins and homocysteine look in normal range (mostly). Is it true that you can be deficient in b6 even though blood work shows you are high? How can you tell if you need more or less in that case? Any advice on a good multivitamin that is methylated, or can you take a regular multi (that still has b vitamins etc) and add in a methylfolate? Thank you so much!
Hello Ashley,
You are most likely not deficient in B6 if your blood levels are high. If you homocysteine is under 9, you are methylating fairly well. For a great methylated multi-vitamin, we use the High Energy Support here: https://store.drjockers.com/products/high-energy-support
Can homocysteine level be too low? What does it mean?
Yes under 4 can indicate a methionine deficiency (possibly due to malabsorption such as Celiac disease) or it could be related to over methylation.