 7 Warning Signs You are Eating Too Many Carbs
7 Warning Signs You are Eating Too Many Carbs
Carbs have a bad rap. But carbs are ultimately not bad. Your body needs carbs and they have some important health benefits. However, eating too many carbs can throw off your blood sugar, increase insulin resistance, and cause all kinds of health issues.
How much carbs and what kind of carbs you consume matter. How you eat your carbs also matters. Today, I want to talk about this: how to avoid eating too many carbs and carb-related health issues and how to eat carbs the healthy and smart way.
In this article, you will learn about the benefits of carbs. You will understand the potential problems with eating much carbs. I will share the 7 signs of eating too many carbs. You will learn about the best sources of carbs. I will share my top tips to balance your blood sugar levels and the best ways to eat carbs. You will learn about the benefits of berberine and alpha lipoic acid for balancing your blood sugar.
Benefits of Carbs
Macronutrients are the nutrients your body needs in larger quantities for energy. They are different from micronutrients (minerals and vitamins), you only need them in smaller amounts. Macronutrients include carbohydrates (carbs), protein, and fats.
Though you often hear about cutting carbs or eating a lower carbohydrate diet for health and weight loss, your body still needs carbs in certain amounts for your health and wellness. Unlike essential amino acids (protein) and essential fatty acids (fats), there are no essential carbohydrates.
However, even though there isn’t such a thing as an essential carb, they can still be helpful as long as the body is insulin sensitive. Carbs offer the body glucose (sugar) to be converted to energy to support physician activities and bodily functions.
Even if you are on and benefit from a very low-carb diet, your diet will still involve some carbs and they offer some essential health benefits. Of course, the types of carbs you eat matter. Whole food sources of carbs include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and beans. Unhealthy sources of carbs include processed food sources, such as pastries, cookies, cakes, candy, and sodas.
But before we look into how to eat carbs and what kind of carbs to eat while staying healthy, let’s look at the potential health benefits of carbs.
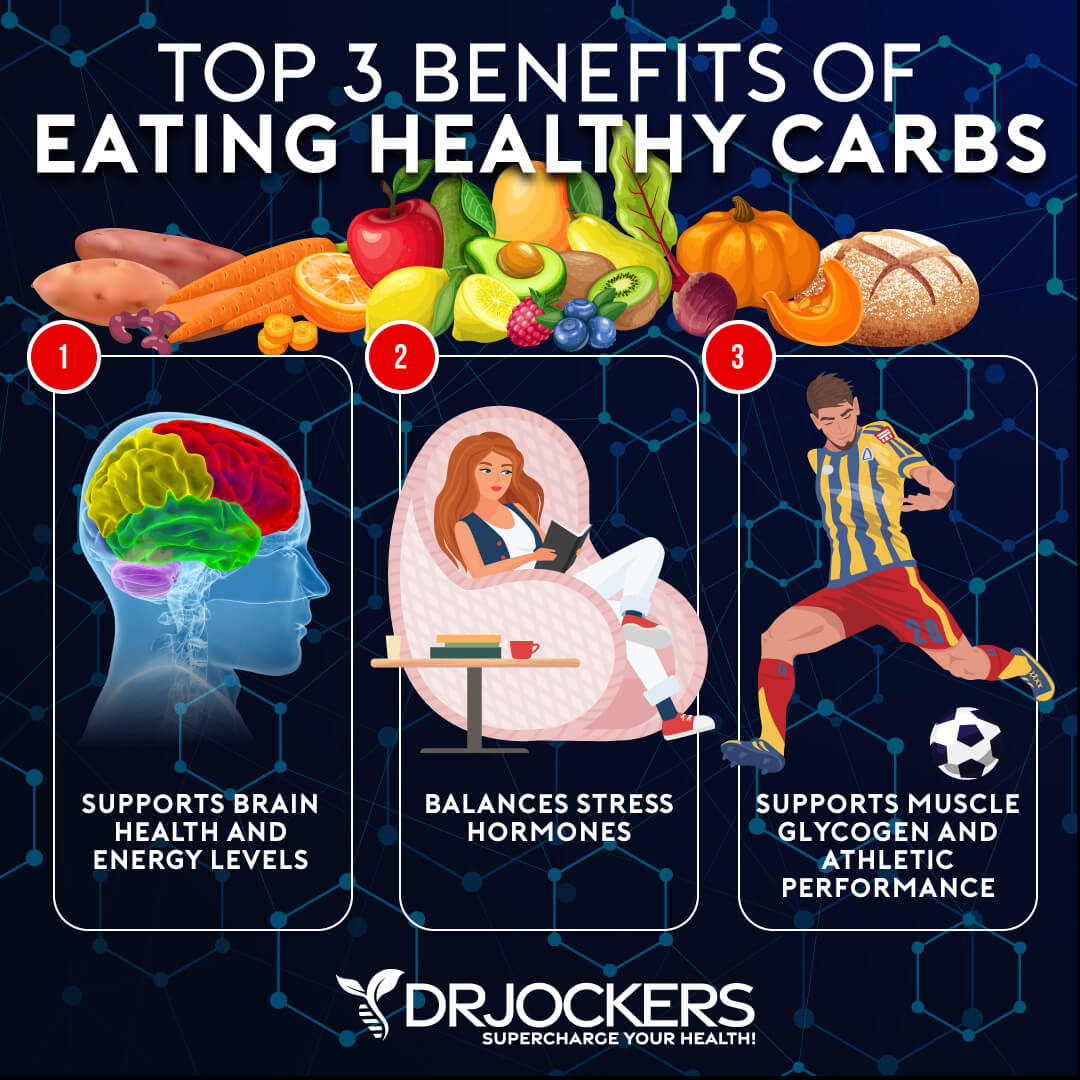
Support Brain Health & Energy Levels
The primary role of carbs is to provide your body with energy. Your body breaks down carbs into glucose. This glucose becomes the main source of energy for your body’s cells, tissues, and organs.
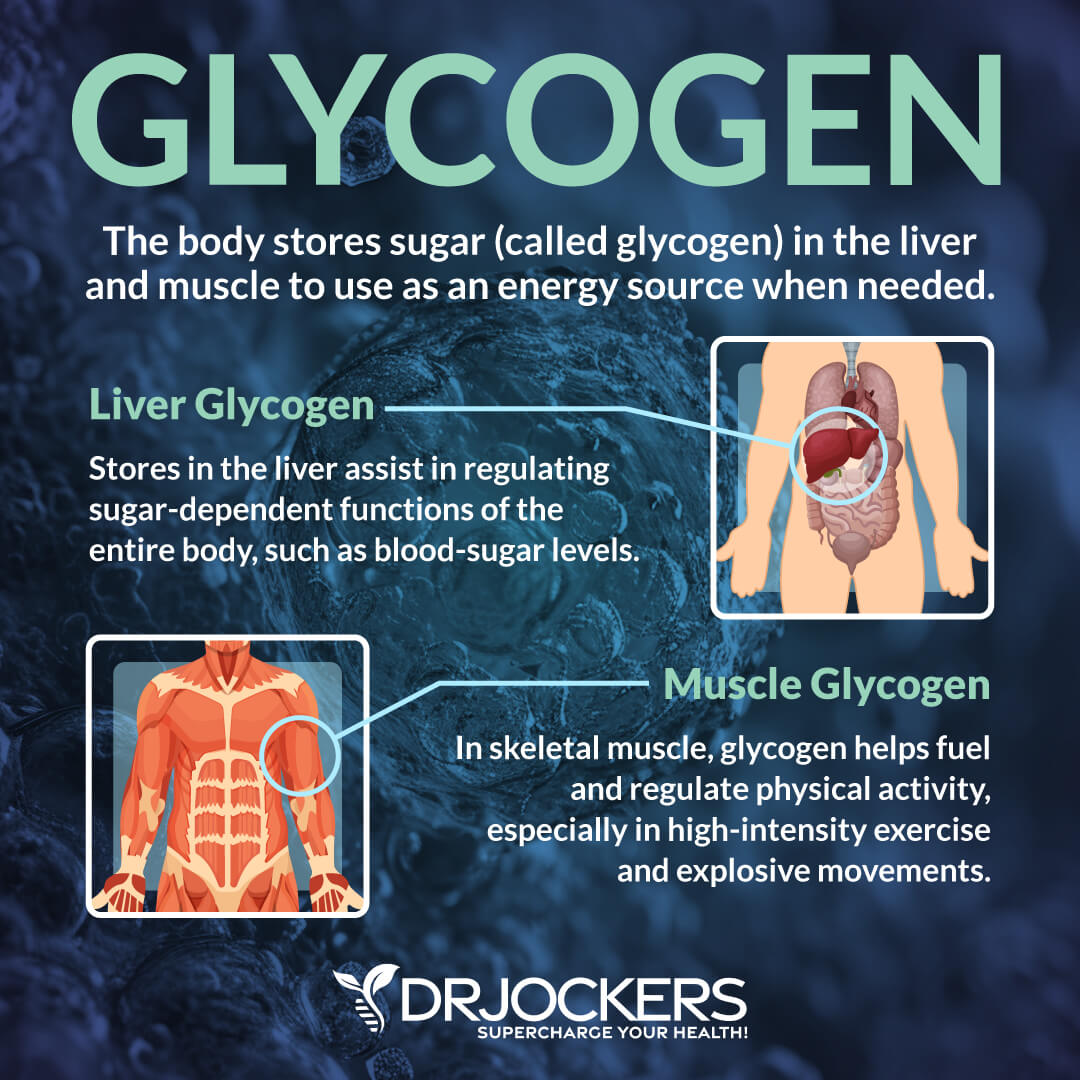
According to the 2023 book Physiology, Carbohydrates, published by Stat Pearls Publishing, carbs help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism and play a role in cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism and fermentation (1). Blood glucose from carbs may be used immediately as energy. Unused glucose gets stored in your muscles and liver for later.
Your brain needs carbohydrates can be really sensitive to blood sugar imbalances. However, the type of carbs matter for your brain and overall health. According to 2021 research published in Clinical Nutrition, eating complex carbs may support memory and benefit the aging brain both short and long term, but simple carbs are linked to decreased cognition (2).
Support Muscle Glycogen & Athletic Performance
Carbs may also support muscle glycogen and athletic performance. Endurance athletes, such as runners and cyclist, particularly love relying on carbohydrates sources for energy and athletic performance.
According to a 2021 meta-analysis published in the Medical and Science in Sports and Exercise, carbohydrates after exercise can support muscle glycogen synthesis, however, the benefits are greater when using both carbs and protein together (3). According to a 2018 review published in Nutrition Today, high-quality carbs may support physical performance (4).
Balance Stress Hormones
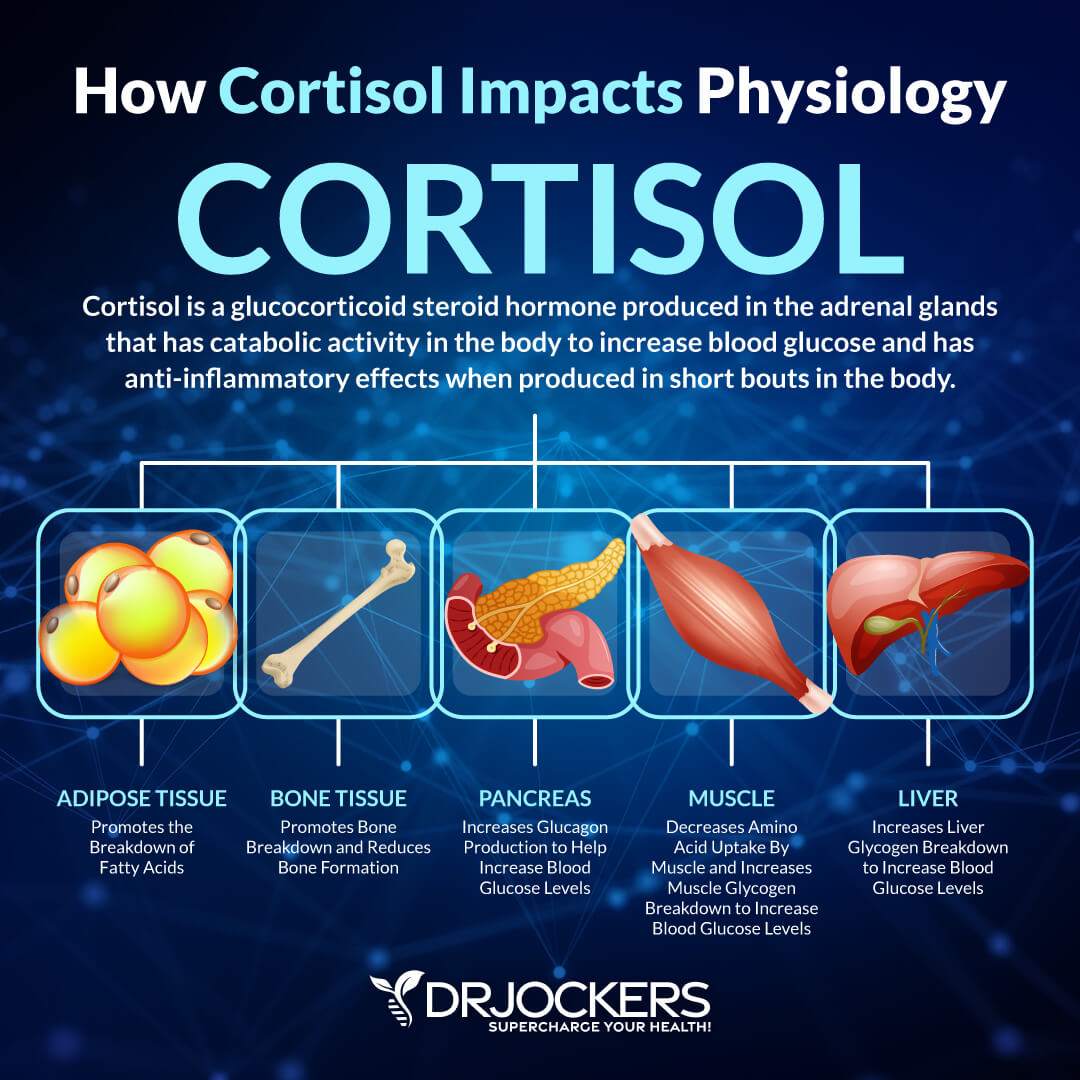
Finally, carbohydrates may help to balance your stress hormones. They may help to lower cortisol and improve hormone function and muscle growth.
According to a 2022 review published in Nutrition and Health, short-term low-carb diets may increase cortisol levels compared to higher-carb diets, though in the long term, these effects may not be the same (5). According to a 2020 diet published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, a higher carb diet may help to reduce cortisol more than a higher fat diet (6).
The Problems with Eating Too Many Carbs
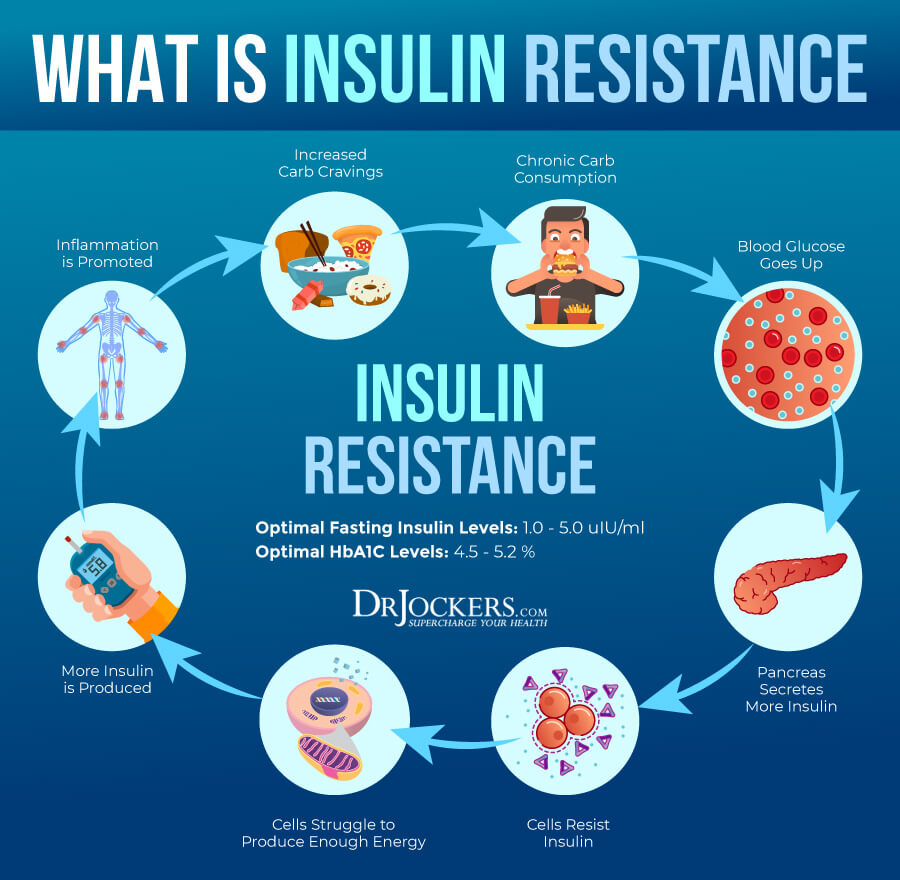
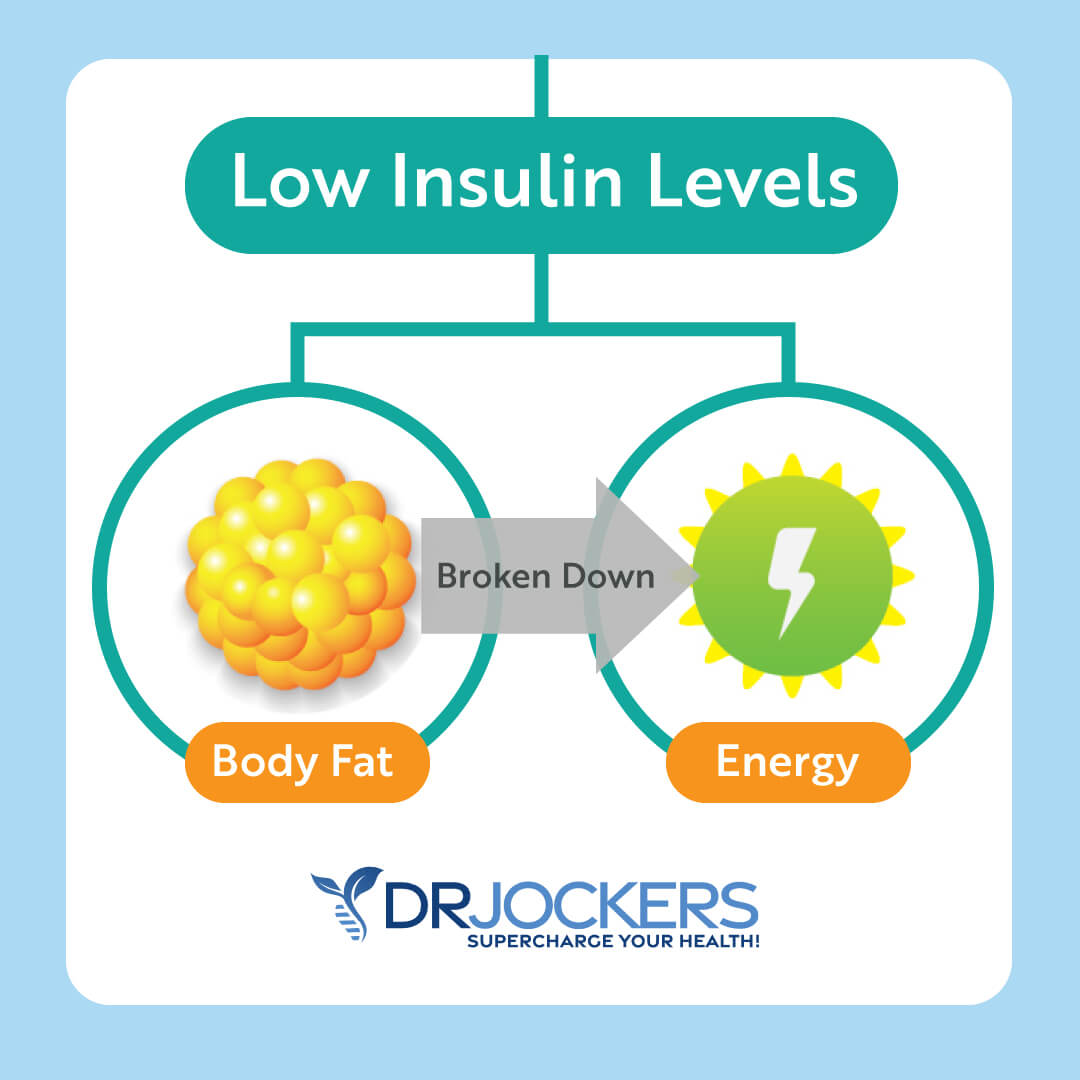
Even though your body needs carbs. If you are eating too many carbs, you can run into some health problems. Eating too many carbs can cause high blood sugar and high insulin levels. If you are eating too many carbohydrates, it may lead to too much insulin in your blood, and too much glucose gets shoved into your cells.
As a result, your cells may lose their sensitivity to insulin. Because of this, insulin won’t be able to move glucose into your cell effectively. Your body will start producing more and more insulin, which can lead to a lot of issues, including increased inflammation, increased fat storage, cravings, hormonal issues, abnormal growth in the body, and so on.

7 Warning Signs of Eating Too Many Carbs
As you see, even though carbs have some health benefits, eating too many carbs and the wrong kind of carbs can turn into a problem, cause high blood sugar and high insulin levels, and lead to other, related health issues. Let’s look at the 7 warning signs of eating too many carbs.
1. Tired After Meals
Being tired after a meal is one sign that you may be eating too many carbs. When we are hungry and consume a meal, we should have plenty of glucose freed up from the meal to get into the cell and provide us with lots of energy.
But if you have insulin resistance, the glucose cannot get into your cells properly. This can lead you to feel tired. Higher levels of insulin can also lead to poor mitochondrial function. As you know, your mitochondria are the powerhouse of your cells and the one that fuels your body with energy.
If the mitochondria are not functioning well, you will feel tired. According to 2010 research published in the Journal of Diabetes Investigation, abnormal mitochondrial function may further disrupt glucose metabolism, leading to a vicious cycle (7).
2. Cravings
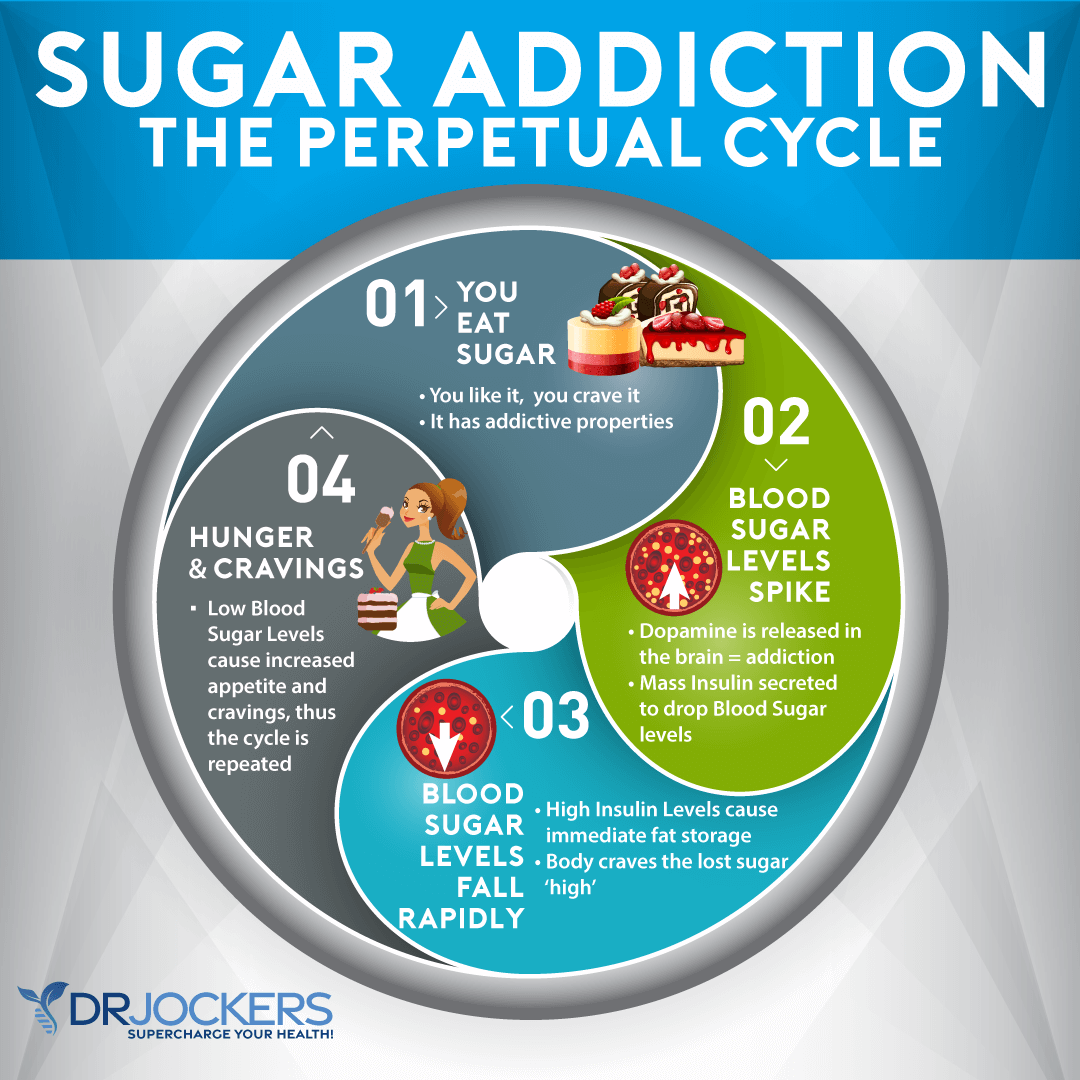
Having cravings after a meal or if you’ve eaten enough is another potential sign of eating too many carbs. If these cravings are for something sweet, it’s especially a huge warning sign. Cravings for sweets are your body’s way of saying that it needs some glucose. This shouldn’t happen after a meal.
After a meal, your body should have enough glucose for energy. If you have insulin resistance and glucose cannot get into the cells. After a meal, you should feel normal, energized, and not hungry. If you have cravings, or trouble going longer between meals, or trouble fasting, it may be a sign of insulin resistance and eating too many carbs.
Moreover, refined sugar may be a particular culprit behind cravings. Processed foods high in sugar are usually also high in unhealthy fats, such as refined oils. According to a 2024 study published in Cell Metabolism, eating foods that are high in sugar and fats, creates a dopamine release, increasing cravings and addiction (8).
Still, sugar is not always the cause of cravings after meals. In other cases, food sensitivities, low stomach acid, and other issues may also cause low energy after meals and cravings.
3. Skin Problems
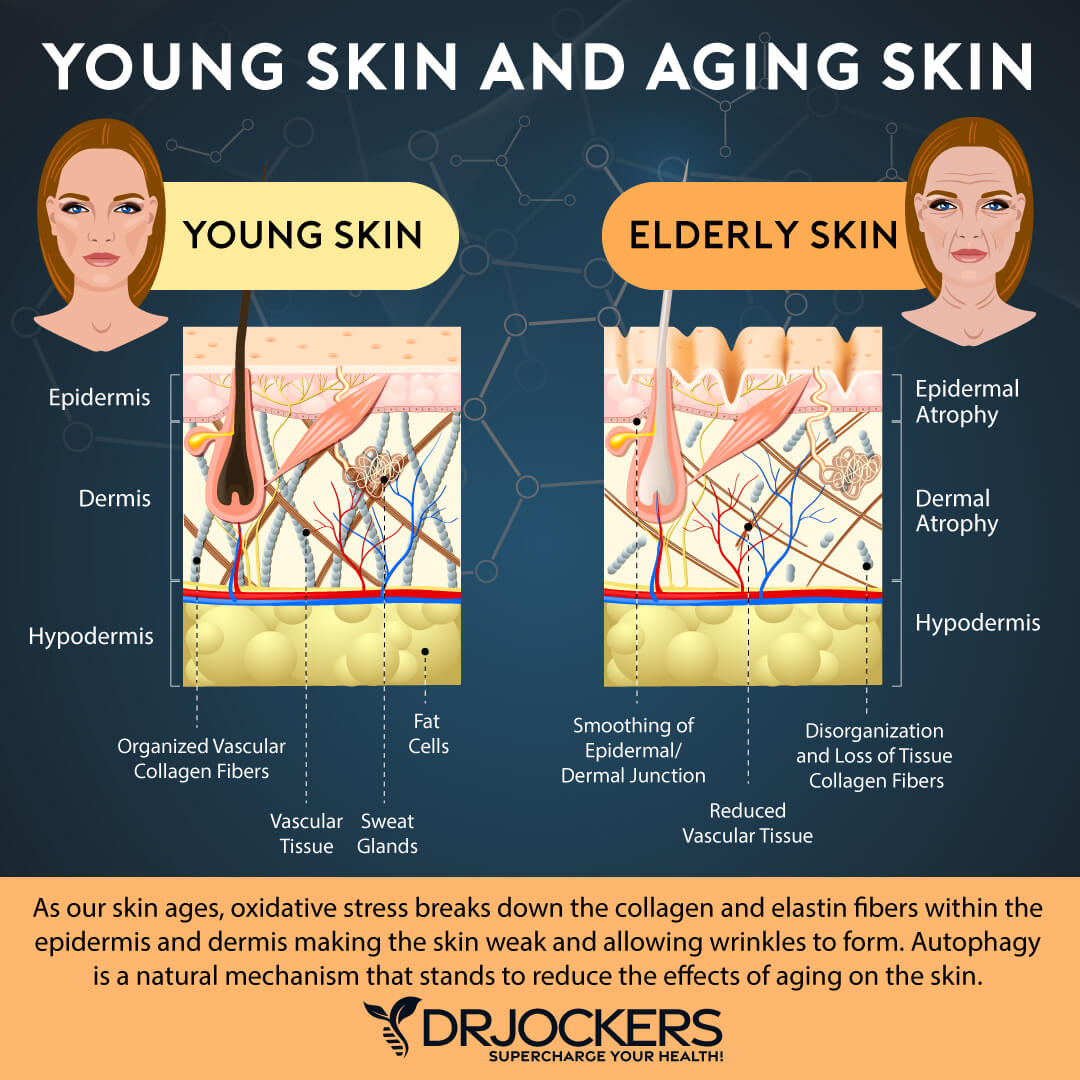
If you are eating too many carbs may also lead to skin problems, particularly acne, skin tags, and skin pigmentation. If you eat too many carbs, your body may start producing too much sebum (oil).
Your skin needs oil, but too much of it can create a breeding ground for skin inflammation. A 2020 study published in Jama Dermatology has linked sugary foods and other unhealthy foods to the risk of adult acne (9).
Insulin resistance may also increase skin inflammation. Skin tags may also mean that too much insulin is sending the message to the skin to grow. A 2010 study published in Anais Brasilienos de Dermatologia has found a strong link between insulin resistance and skin tags (10).
Skin pigmentation may be a sign of oxidative stress, which is a byproduct of glycolytic energy storage. A 2022 study published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology has found that sugar may increase oxidative stress and inflammatory skin diseases (11).
4. Hormone Problems
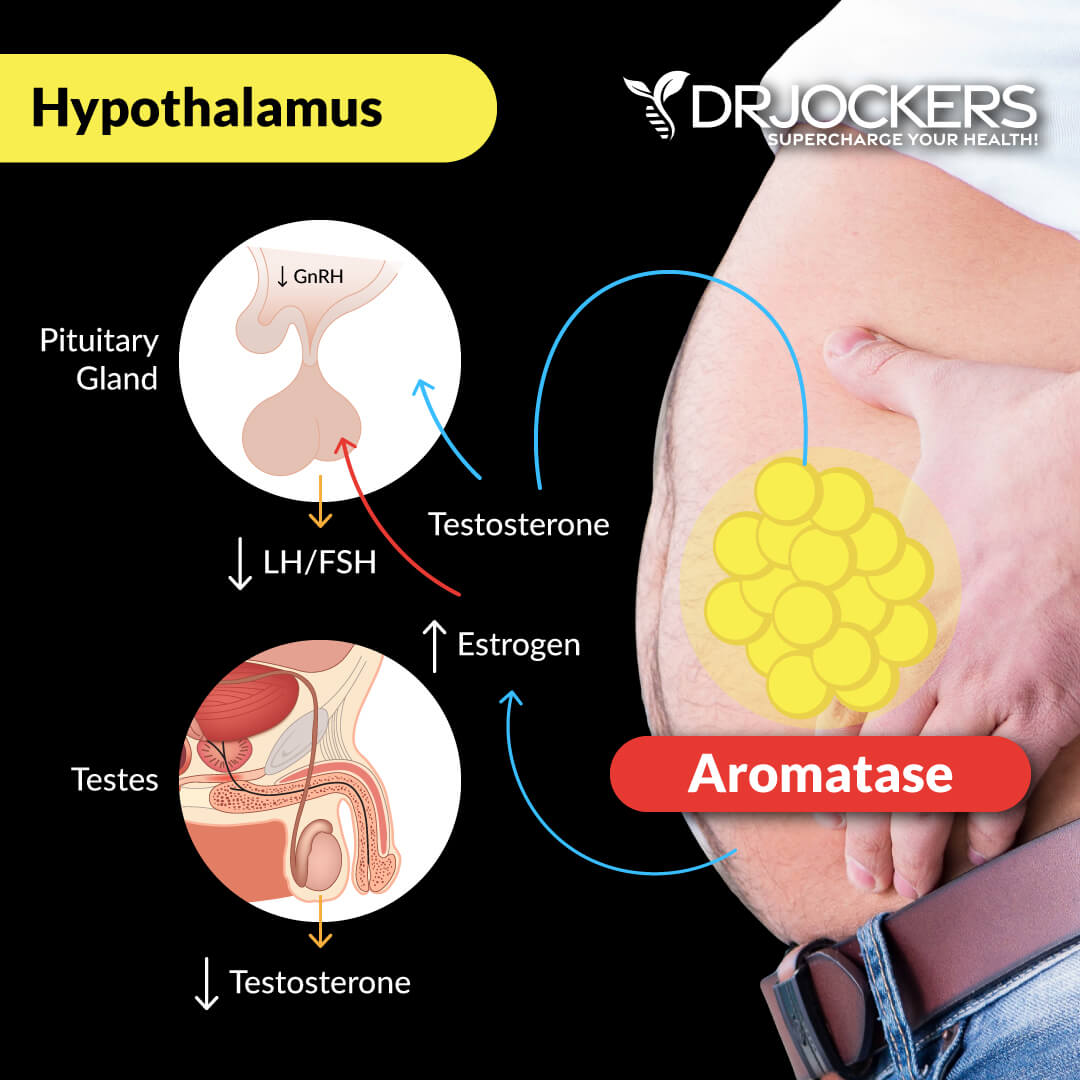
Eating too many carbs may cause hormonal problems. According to a 2018 study published in Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, drinking high-sugar drinks can seriously impact the testosterone levels of men between 20 and 39 (12).
When insulin is elevated, it may increase aromatase that can convert testosterone into estrogen. This can lead to andropause or low testosterone and related issues, such as low libido, prostate issues, and poor mental health.
In women, sugar may cause excess estrogen or excess testosterone production. PCOS is associated with insulin resistance and higher testosterone, and endometriosis with higher estrogen.
Hormonal imbalances and increased testosterone and/or estrogen in women may increase the risk of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and other hormonal issues. According to a 2017 study published in the Journal of Endocrine Society, a high-sugar, high-fat diet can disrupt the increase of preovulatory hormones, increasing the risk of ovarian cysts in women (13).
5. Trouble Losing Weight
A 2020 study published in Nutrients has linked a high carbohydrate intake to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome and obesity (14). Insulin is a fat-storage hormone that stops your body from burning fat. If you are eating too many carbs and have insulin resistance it may cause your body to store more fat, especially visceral fat. It may lead to trouble losing weight.
Moreover, a high-carb diet may cause cravings, which may lead to more sugar and more calorie consumption beyond your needs. This can cause weight gain. And, of course, carb and sugar addiction or overeating on carbs will interfere with your weight loss goals.
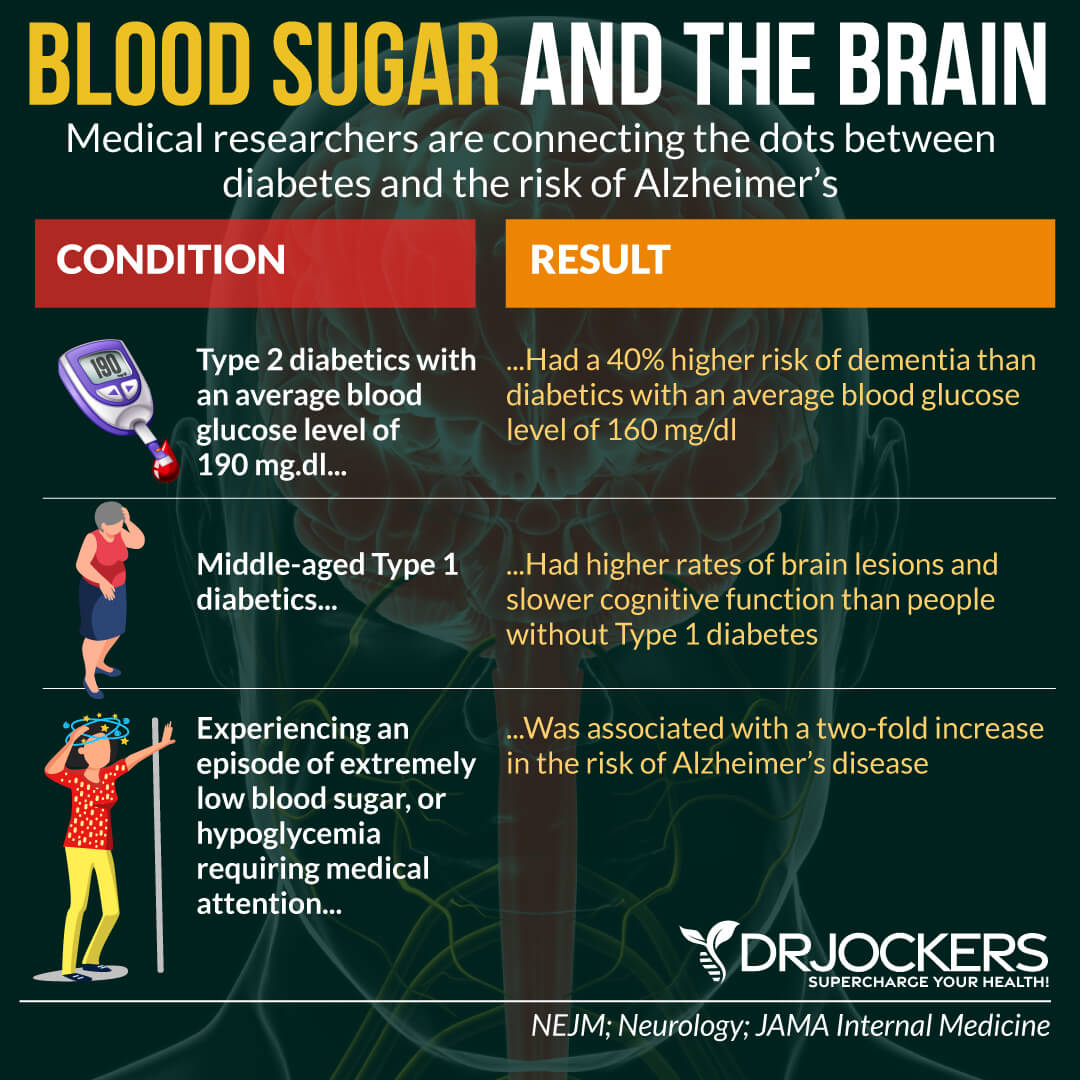
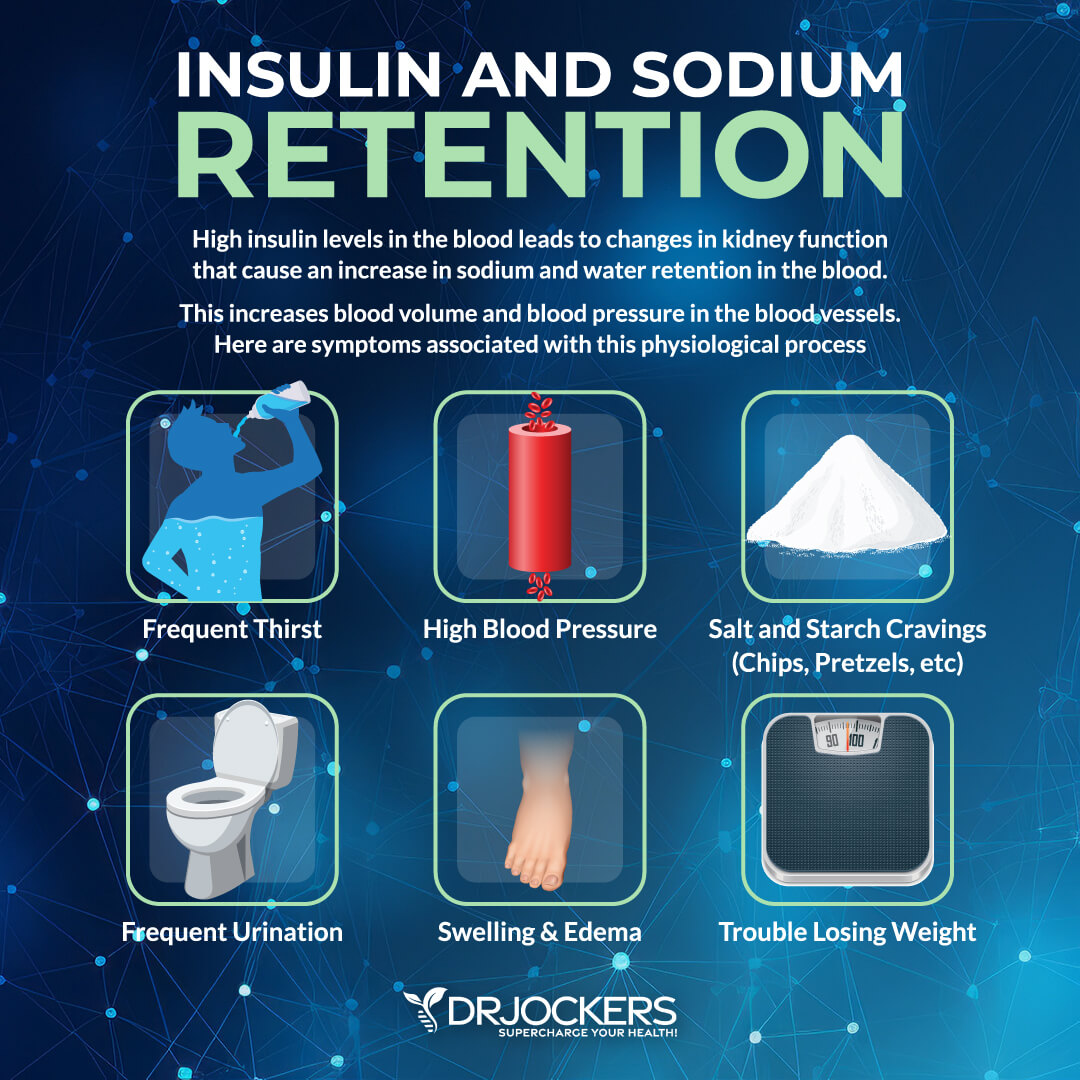
6. Frequent Thirst
Frequent thirst may also be a sign of eating too many carbs. According to 2023 research published in Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology, frequent thirst and increased urination may also be a sign of insulin resistance and diabetes (15).
Glucose goes into the cells with water. When you have higher insulin, your body will retain more water and more sodium. This means you will be thirstier. Eating too much sugar can increase toxicity and AGEs.
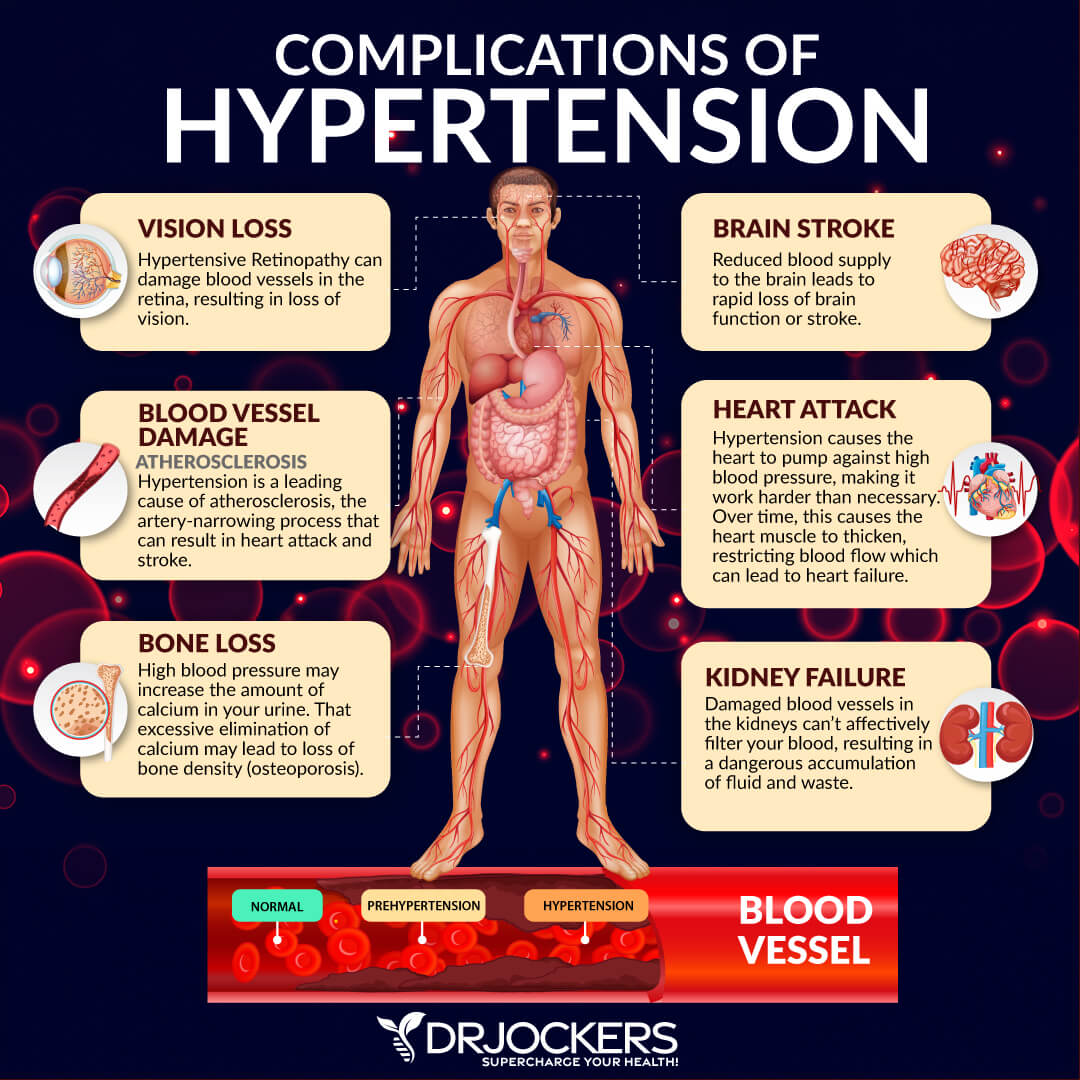
7. High Blood Pressure & Triglycerides
Finally, high blood pressure and high triglycerides may also be a sign of eating too many carbs. A 2014 review published in Open Heart has found that a high sugar intake may increase the risk of high blood pressure and cardiometabolic disease (16).
Insulin causes sodium and water retention. Insulin can also increase blood volume, but too much insulin can also increase blood volume and blood pressure. Too many carbs can also cause the blood vessels to lose their elasticity.
They may become rigid, so they won’t be able to flex when the heart beats. If it cannot flex, it can increase all kinds of cardiovascular issues as well as neurodegeneration and cognitive issues.
Best Carb Sources
If you eat carbs, it’s important that you eat carbs from healthy, whole food sources, such as fruits (e.g., berries, apples, pears, oranges, grapefruits, pineapple, etc.), root vegetables (e.g., carrots, beets, radishes, yams, sweet potatoes, etc.), and fermented grains, such as sourdough bread.
These carb sources all contain helpful nutrients, support the gut microbiome, and are less insulogenic than processed carbs.

How to Stabilize Blood Sugar Levels
Besides choosing healthy carbs, I recommend that you follow some strategies to stabilize your blood sugar levels. To learn about these tips in more detail, I recommend reading this article.
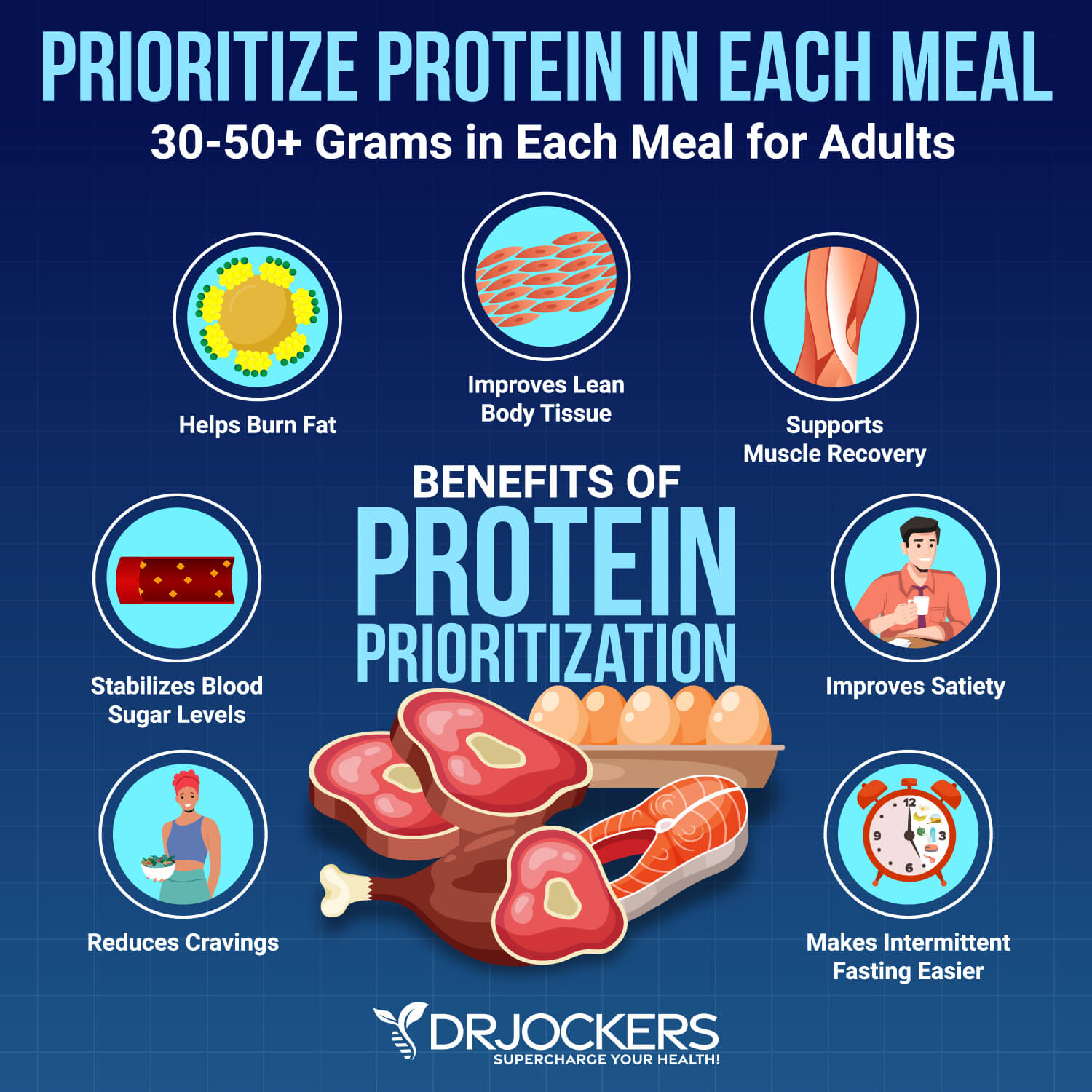
Eat 30 – 50+ Grams of Protein in Each Meal
If you are eating carbs, I recommend eating some protein in the same meal. I recommend consuming 30 to 50 grams of protein with each meal. I recommend getting 30 to 50 grams of protein or more each meal. A 2021 study published in the Iranian Journal of Public Health has found that eating protein with your meals may help to balance your blood sugar levels (9).
Eating enough protein with each meal may also help to reduce your cravings for sugary and unhealthy foods and energize your body. Healthy protein sources include grass-fed meat, pasture-raised poultry and eggs, wild-caught fish and seafood, wild game, nuts, and seeds.
Eat at Least 15-20 Grams of Healthy Fats in Each Meal
Besides protein, it’s just as important to eat healthy fats along with carbs. I recommend eating at least 15 to 20 grams of healthy fats with each meal.
According to a 2020 meta-analysis published in Cureus, a high-fat, low-carb ketogenic diet may help to improve fasting blood sugar levels, improve fasting insulin levels, support weight loss, improve cholesterol levels, and improve diabetes (18). Healthy fats include avocados, avocado oil, olives, extra-virgin olive oil, extra-virgin coconut oil, coconut milk, MCT oil, wild-caught fish and seafood, flax seeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds.
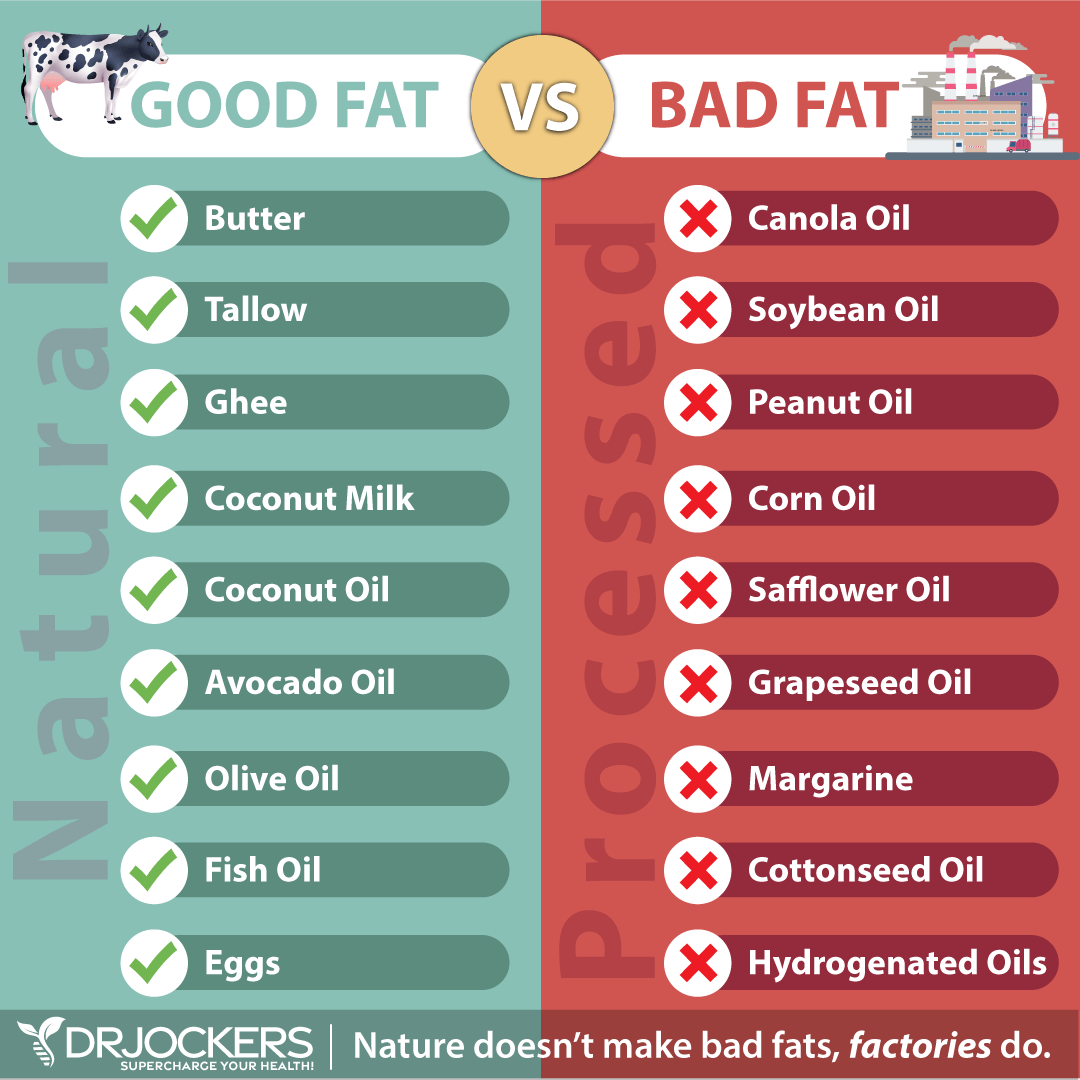
Avoid Processed Carbs and Naked Carbs
I also recommend avoiding processed carbs and naked carbs. Processed carbs you should avoid include cakes, pastries, bread, pasta, candy, or ice cream. These are essential empty calories without nutritional values.
Also, avoid eating carbs without protein and fats on the side. This what I call naked carbs. Examples of naked carbs include eating potatoes or bread without much or any fats or protein.

Go For a Walk After Meals
Going for a walk after a meal can also help to balance your blood sugar levels. It doesn’t even have to be long.
According to a 2022 systematic review and meta-analysis published in Sports Medicine, even 2 to 5 minutes of walking after a meal may help to improve your blood sugar and cardiometabolic markers (19). A short stroll after your meals can turn into a great family activity or time to catch up with colleagues or friends. It may turn into a form of movement meditation.

Eat Protein & Fiber Before Carbs
Eating your protein and fiber before carbs is another great idea to balance your blood sugar levels, improve satiety, reduce cravings, and prevent overeating.
According to a 2020 study published in Nutrients, eating fiber along with your meals, before carbs, may help to balance blood sugar levels and manage or reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes (20). Not to mention that vegetables are full of micronutrients that nourish your body and reduce cravings.
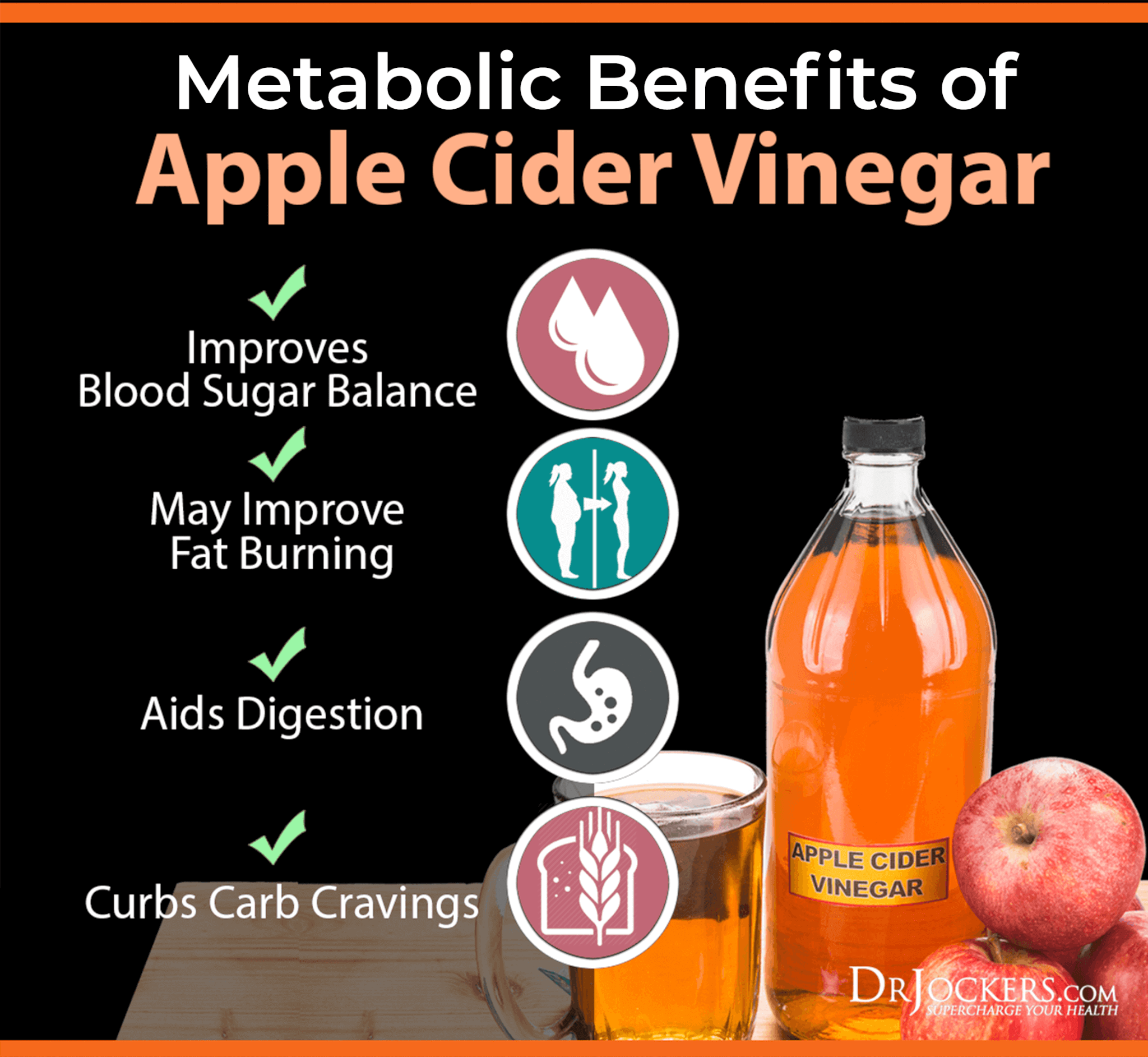
Use ACV or Lemon Juice with Meals
Adding a tabletop of apple cider vinegar to water or squeezing some lemon juice into water and drinking it with your meals is another great tip for balancing your blood sugar.
According to a 2019 review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Advanced Nursing, apple cider vinegar may have beneficial effects on blood sugar and glycemic control in those with type 2 diabetes (21). A 2021 study published in the European Journal of Nutrition; lemon juice may also help to reduce the glycemic response after carbohydrate-heavy foods (22).
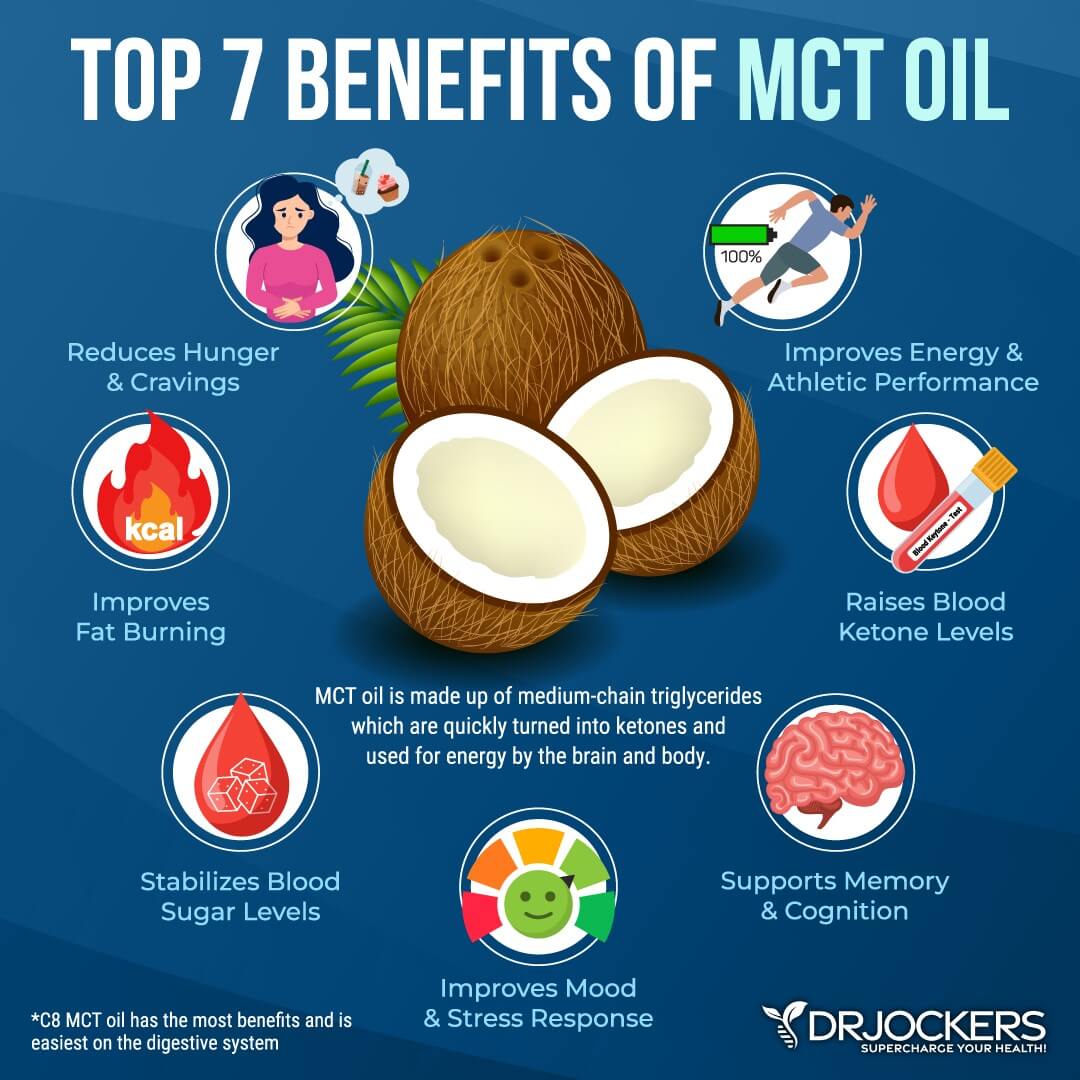
Have MCT Oil with Meals
Finally, I recommend using MCT oil. It is one source of healthy fats that may help to balance your blood sugar.
A 2019 study published in PLoS One has found that using MCT oil may help to improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar (23). I recommend using MCT oil with your meals for better blood sugar balance.
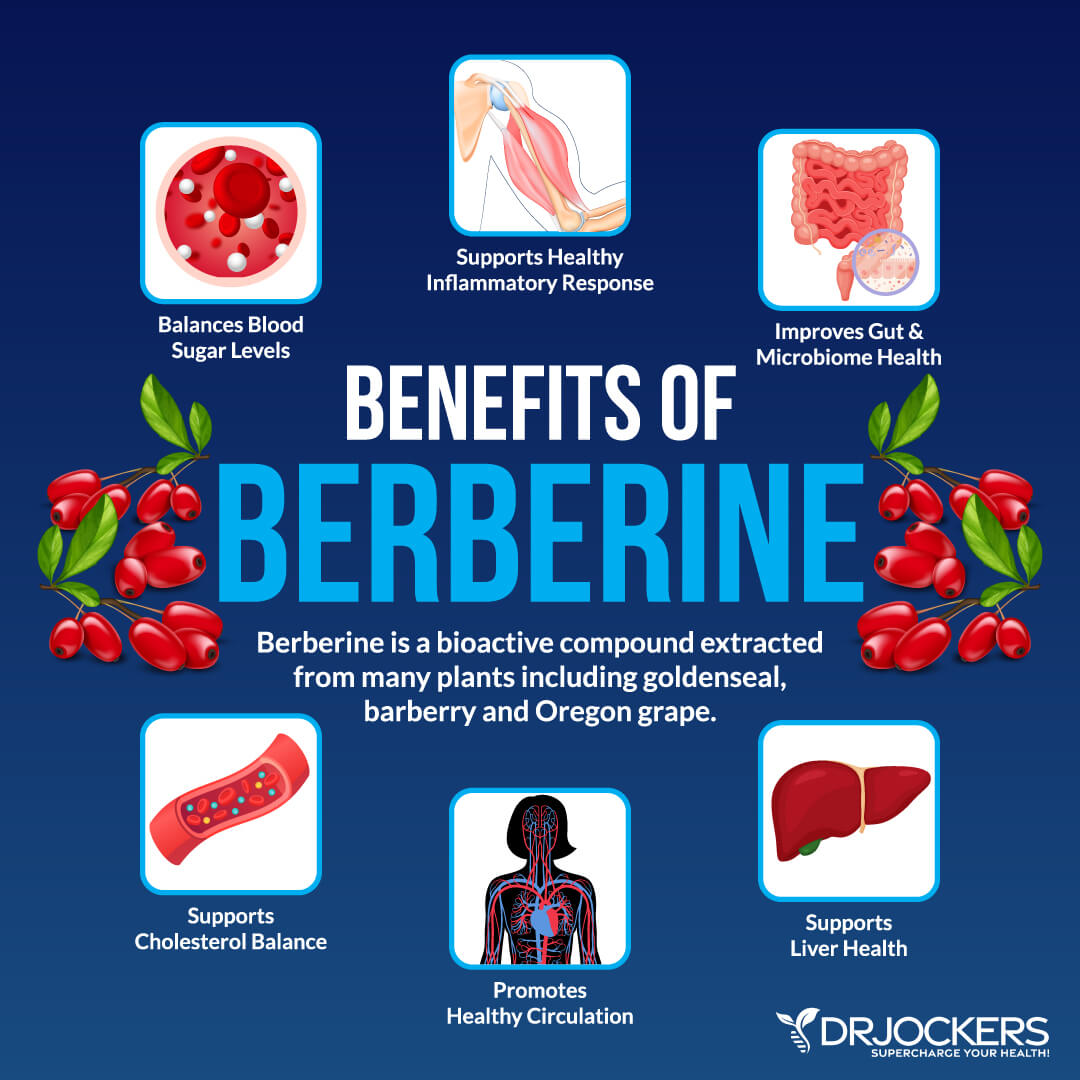
Using Berberine & Alpha Lipoic Acid
I also recommend using berberine and alpha lipoic acid to balance your blood sugar levels. Berberine is a nutrient found in European barberry, Oregon grape, goldenseal, tree turmeric, and some other plants. It has a yellow color and bitter taste.
It is commonly used as herbal support for various issues, including to balance blood sugar, aid diabetes treatment, support weight loss, support heart health, decrease blood pressure, reduce cholesterol, improve liver health, improve burns, and for other uses.
A 2008 study published in Metabolism has found that berberine may help to reduce HbA1c levels in diabetes (24). You may benefit from supplementing with berberine for balancing your blood sugar.
Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is an antioxidant. It is naturally made by your body and synthesized by your mitochondria. It serves as a cofactor for the enzymatic breakdown of nutrients. It can also be found in some foods, including beets, potatoes, carrots, broccoli, spinach, and red meat.
According to 2022 research published in Nutrients, alpha lipoic acid may help the regulation of insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, and glucose metabolism (25). It may be beneficial for people with insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and PCOS.

Introducing Glycemic Synergy
To benefit from berberine and alpha lipoic acid, I recommend using Glycemic Synergy. It is a targeted formula designed to help support healthy blood sugar metabolism and antioxidative status.
Combined, berberine and ALA may provide synergistic properties to help promote healthy metabolism. Glycemic Synergy may help support normal blood sugar metabolism, healthy cardiovascular function, antioxidative status, and cellular health.
Final Thoughts
Carbs are ultimately not bad. Your body needs carbs and they have some important health benefits. However, eating too many carbs can throw off your blood sugar, increase insulin resistance, and cause all kinds of health issues.
How much carbs and what kind of carbs you eat and how you eat them matter. Follow my tips in this article on how to avoid eating too many carbs, how to balance your blood sugar, and how to eat carbs in a healthy and smart way.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. Our website offers long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out and our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!





Good info to follow.
Please proofread before posting as there are several grammatical errors throughout the article.